57. 插入区间
57. 插入区间
题目
You are given an array of non-overlapping intervals intervals where intervals[i] = [starti, endi] represent the start and the end of the ith interval and intervals is sorted in ascending order by starti. You are also given an interval newInterval = [start, end] that represents the start and end of another interval.
Insert newInterval into intervals such that intervals is still sorted in ascending order by starti and intervals still does not have any overlapping intervals (merge overlapping intervals if necessary).
Return intervals after the insertion.
Example 1:
Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
Example 2:
Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]]
Explanation: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
Constraints:
0 <= intervals.length <= 10^4intervals[i].length == 20 <= starti <= endi <= 10^5intervalsis sorted bystartiin ascending order.newInterval.length == 20 <= start <= end <= 10^5
题目大意
给你一个 无重叠的 ,按照区间起始端点排序的区间列表 intervals,其中 intervals[i] = [starti, endi] 表示第 i 个区间的开始和结束,并且 intervals 按照 starti 升序排列。同样给定一个区间 newInterval = [start, end] 表示另一个区间的开始和结束。
在 intervals 中插入区间 newInterval,使得 intervals 依然按照 starti 升序排列,且区间之间不重叠(如果有必要的话,可以合并区间)。
返回插入之后的 intervals。
注意 你不需要原地修改 intervals。你可以创建一个新数组然后返回它。
解题思路
- 遍历区间数组,取出当前区间
[b1, b2],依次与插入区间[a1, a2]对比,可能有如下三种情况:
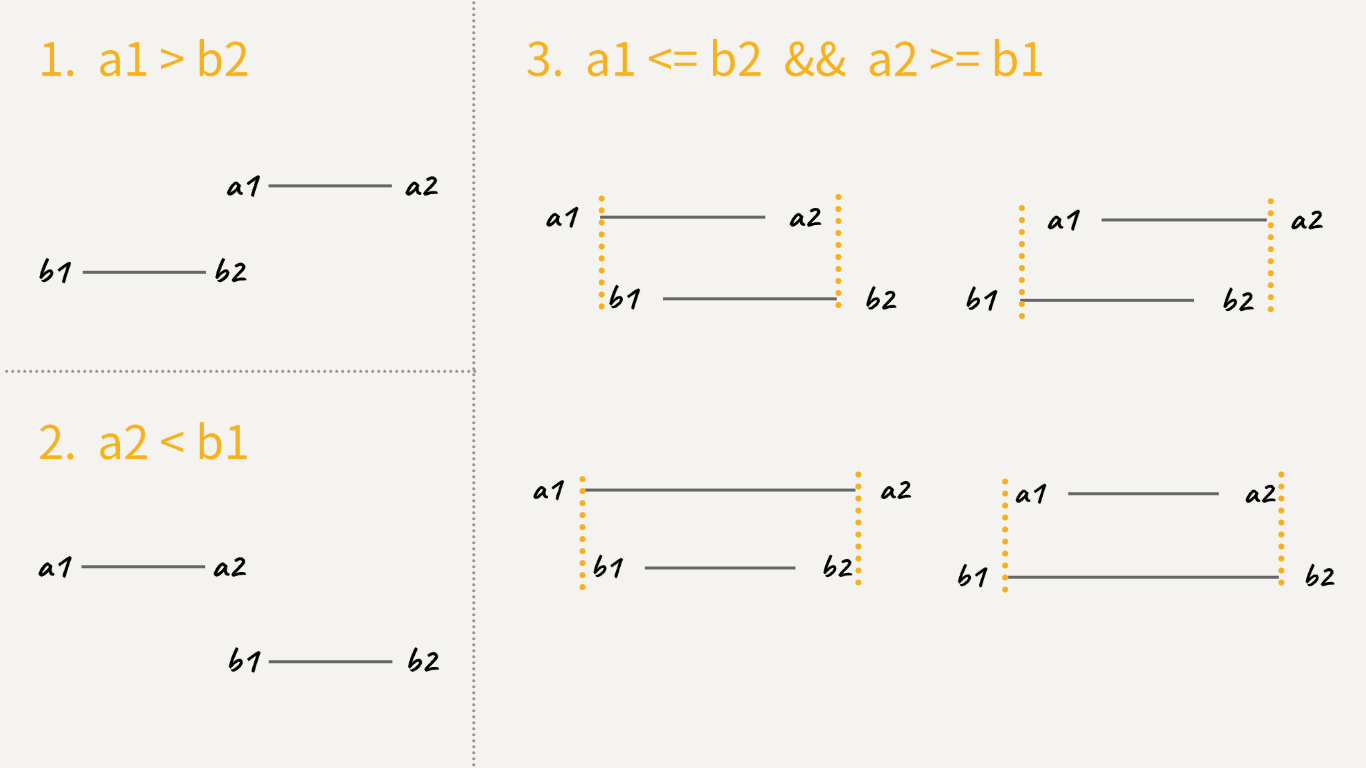
- 情况一,两区间不相交且
a1 > b2,直接将当前区间[b1, b2]放入返回数组,继续对比后续区间; - 情况二,两区间不相交且
a2 < b1,说明已经找到了插入区间[a1, a2]的位置,将插入区间和后续没有对比过的区间都放入返回数组,并跳出循环; - 情况三,两个区间相交,此时需要将两个区间合并,将合并后的区间作为新的插入区间与后续区间对比。合并后的区间分为四种情况,根据上图可以发现规律,只需更新
a1和a2为:a1 = min(a1, b1)a2 = max(a2, b2)
- 注意边界情况
- 若区间数组为空(例如:
intervals = [], newInterval = [1,2]),则直接返回newInterval;
- 若区间数组为空(例如:
- 当循环遍历到区间数组的最后一个时(例如:
intervals = [[2,3]], newInterval = [1,4]),由于后面不会再出现情况 2 了,所以最后要将合并后的区间放入返回数组中。
- 当循环遍历到区间数组的最后一个时(例如:
代码
/**
* @param {number[][]} intervals
* @param {number[]} newInterval
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var insert = function (intervals, newInterval) {
// 边界情况一
if (intervals.length == 0) return [newInterval];
let res = [],
a1 = newInterval[0],
a2 = newInterval[1];
for (let i = 0; i < intervals.length; i++) {
let b1 = intervals[i][0],
b2 = intervals[i][1];
// 情况一
if (a1 > b2) {
res.push(intervals[i]);
}
// 情况二
else if (a2 < b1) {
res.push([a1, a2]);
res.push(...intervals.slice(i, intervals.length));
break;
}
// 情况三
else {
a1 = Math.min(a1, b1);
a2 = Math.max(a2, b2);
}
// 边界情况二
if (i == intervals.length - 1) {
res.push([a1, a2]);
}
}
return res;
};
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 56 | 合并区间 | [✓] | 数组 排序 | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 715 | Range 模块 | 设计 线段树 有序集合 | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 2276 | 统计区间中的整数数目 | 设计 线段树 有序集合 | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
