2.4 队列
2.4 队列
队列的定义
定义
队列(Queue) :一种线性表数据结构,是一种只允许在表的一端进行插入操作,而在表的另一端进行删除操作的线性表。
先进者先出,这就是典型的“队列”。你可以把它想象成排队买票,先来的先买,后来的人只能站末尾,不允许插队。
队列跟栈一样,也是一种操作受限的线性表数据结构,栈只支持两个基本操作:入栈 push() 和出栈 pop()。队列最基本的操作也是两个:入队 enQueue(),放一个数据到队列尾部;出队 deQueue(),从队列头部取一个元素。

我们把队列中允许插入的一端称为 队尾(rear);把允许删除的另一端称为 队头(front)。当表中没有任何数据元素时,称之为 空队。
我们可以从两个方面来解释一下队列的定义:
「线性表」
队列首先是一个线性表,队列中元素具有前驱后继的线性关系。队列中元素按照
a1,a2,...,an的次序依次入队。队头元素为a1,队尾元素为an。「先进先出原则」
元素进入队列或者退出队列是按照 「先进先出(First In First Out)」 的原则进行的,最先进入队列的元素在队头,最后进入队列的元素在队尾。每次从队列中删除的总是队头元素,即最先进入队列的元素。
队列的实现
跟栈一样,队列可以用数组来实现,也可以用链表来实现。
用数组实现的栈叫作顺序栈,用链表实现的栈叫作链式栈。
同样,用数组实现的队列叫作顺序队列,用链表实现的队列叫作链式队列。
顺序队列
class ArrayQueue {
constructor() {
this._queue = [];
}
// 入队
enQueue(data) {
this._queue.push(data);
}
// 出队
deQueue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('This queue is empty');
return null;
}
return this._queue.shift();
}
// 判断是否为空队
isEmpty() {
return this._queue.length === 0;
}
// 查看队头元素
front() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('This queue is empty');
return null;
}
return this._queue[0];
}
// 查看队尾元素
rear() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('This queue is empty');
return null;
}
return this._queue[this.count() - 1];
}
// 清空队列
clear() {
delete this._queue;
this._queue = [];
}
// 打印队列
print() {
console.log(this._queue);
}
// 获取队列中元素的数量
count() {
return this._queue.length;
}
// 将队列中元素以字符串形式返回
toString() {
return this._queue.join(',');
}
}
👉 查看代码测试 👈
const queue = new ArrayQueue();
queue.enQueue(1);
queue.enQueue(2);
queue.enQueue(3);
queue.print(); // output: [1, 2, 3]
console.log(queue.front()); // output: 1
console.log(queue.rear()); // output: 3
queue.deQueue();
queue.print(); // output: [2, 3]
console.log(queue.count()); // output: 2
console.log(queue.isEmpty()); // output: false
console.log(queue.toString()); // output: 2,3
链式队列
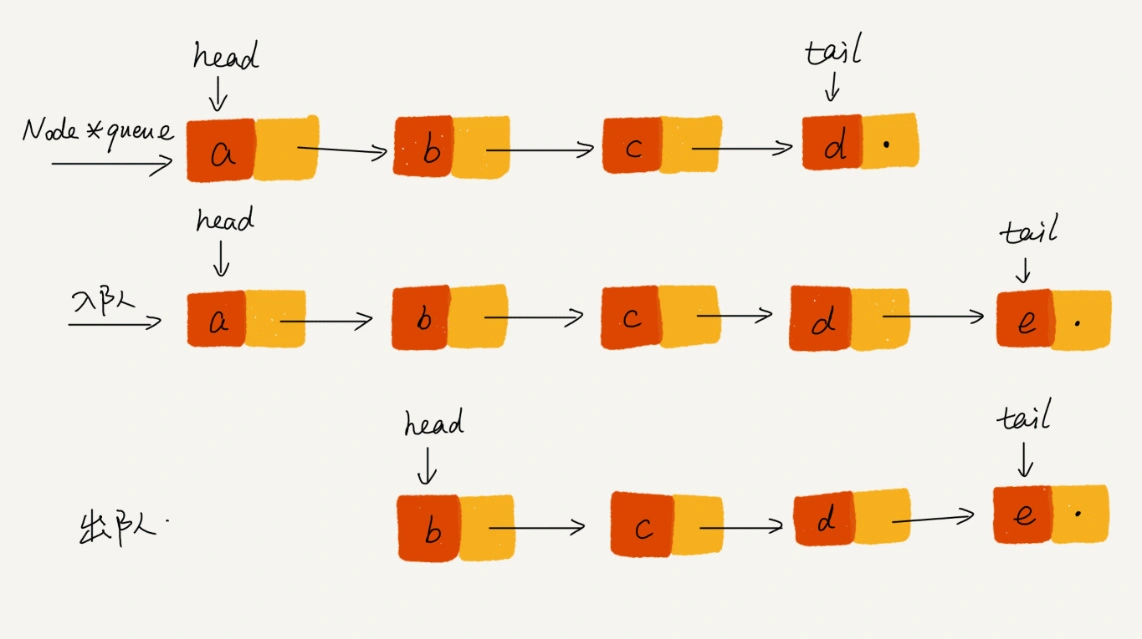
基于链表的实现,需要两个指针: head 指针和 tail 指针。它们分别指向链表的第一个结点和最后一个结点。
如图所示:
- 入队时:
tail.next= new_node, tail = tail.next - 出队时:
head = head.next
class Node {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data; // 节点中的数据
this.next = null; // 下一个节点
}
}
class LinkedListQueue {
constructor() {
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// 入队
enQueue(data) {
const node = new Node(data);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = this.tail.next;
}
this.length++;
}
// 出队
deQueue() {
if (this.isEmpty()) return null;
let cur = this.head;
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return cur;
}
// 判断是否为空队
isEmpty() {
return this.length === 0;
}
// 查看队头元素
front() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('This queue is empty');
return null;
}
return this.head.data;
}
// 查看队尾元素
rear() {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
console.log('This queue is empty');
return null;
}
return this.tail.data;
}
// 清空队列
clear() {
this.tail = null;
this.head.next = null;
this.head = null;
this.length = 0;
}
// 打印队列
print() {
console.log(this.head);
}
// 获取队列中元素的数量
count() {
return this.length;
}
// 将队列中元素以字符串形式返回
toString() {
let res = [];
let prev = this.head;
while (prev) {
res.push(prev.data);
prev = prev.next;
}
return res.join(',');
}
}
👉 查看代码测试 👈
const queue = new LinkedListQueue();
queue.enQueue(1);
queue.enQueue(2);
queue.enQueue(3);
queue.deQueue();
queue.print();
// output: Node {data: 2, next: Node {data: 3, next: null}}
console.log(queue.count()); // output: 2
console.log(queue.front()); // output: 2
console.log(queue.rear()); // output: 3
console.log(queue.isEmpty()); // output: false
console.log(queue.toString()); // output: 2,3
循环队列
定义
循环队列(Circular Queue) 是一种线性数据结构,其操作表现基于 FIFO(先进先出)原则,并且队尾被连接在队首之后,以形成一个循环。它也被称为“环形缓冲器”。
在基于数组实现的顺序队列中,由于出队操作总是删除当前的队头元素,将 front 进行右移,而插入操作又总是在队尾进行。经过不断的出队、入队操作,队列的变化就像是使队列整体向右移动。
当队尾指针指向最右边时,即使在队列前面仍有空闲空间,也无法继续往队列中添加数据了,之前因为出队操作而产生空余位置没有利用上,这就造成了 假溢出 问题。
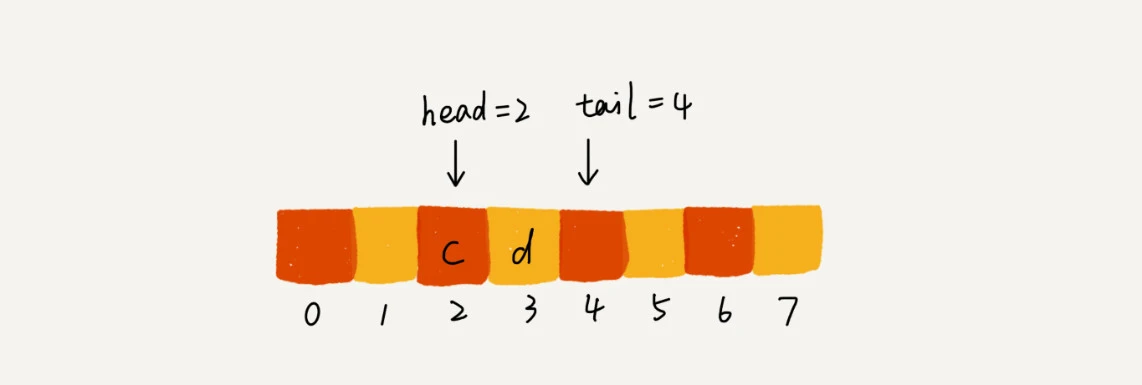
为了解决这个问题,我们可以将队列想象成为头尾相连的循环表。原本数组是有头有尾的,是一条直线。把首尾相连之后,被扳成了一个环,利用数学中的求模运算,我们能使用这些前面的空闲空间去存储新的值。

📌 622. 设计循环队列 - LeetCode
💻 题目大意
设计循环队列,支持如下操作:
MyCircularQueue(k): 构造器,设置队列长度为k;Front: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回-1;Rear: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回-1;enQueue(value): 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真;deQueue(): 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真;isEmpty(): 检查循环队列是否为空;isFull(): 检查循环队列是否已满;
示例:
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
说明:
- 所有的值都在
0至1000的范围内; - 操作数将在
1至1000的范围内; - 请不要使用内置的队列库。
💎 代码
/**
* @param {number} k
*/
var MyCircularQueue = function (k) {
this.queue = new Array(k);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.size = k;
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.enQueue = function (value) {
if (this.isFull()) return false;
this.queue[this.tail] = value;
// 将 tail 指向队尾的下一个空间
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % this.size;
return true;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.deQueue = function () {
if (this.isEmpty()) return false;
this.queue[this.head] = null;
// 将 head 指向新的队头
this.head = (this.head + 1) % this.size;
return true;
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Front = function () {
return this.isEmpty() ? -1 : this.queue[this.head];
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Rear = function () {
// 因为 tail 指向队尾的下一个空间,所以要分情况处理
// 若 tail == 0,那队尾应该在 size - 1
// 其他情况,队尾在 tail - 1
let index = this.tail === 0 ? this.size - 1 : this.tail - 1;
return this.isEmpty() ? -1 : this.queue[index];
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
// head == tail 时,有两种情况
// 一种是队列为空,此时 queue[head] 为null
// 一种是队列满了,此时 queue[head] 有值
return this.head === this.tail && !this.queue[this.head];
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isFull = function () {
return this.head === this.tail && !!this.queue[this.head];
};
#### 📌 [622. 设计循环队列 - LeetCode](https://wangfuyou.com/leetcode-js/problem/0622.html)
#### 💻 **题目大意**
设计循环队列,支持如下操作:
- `MyCircularQueue(k)`: 构造器,设置队列长度为 `k` ;
- `Front`: 从队首获取元素。如果队列为空,返回 `-1` ;
- `Rear`: 获取队尾元素。如果队列为空,返回 `-1` ;
- `enQueue(value)`: 向循环队列插入一个元素。如果成功插入则返回真;
- `deQueue()`: 从循环队列中删除一个元素。如果成功删除则返回真;
- `isEmpty()`: 检查循环队列是否为空;
- `isFull()`: 检查循环队列是否已满;
**示例**:
```javascript
MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3
circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3
circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true
circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true
circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
```
**说明**:
- 所有的值都在 `0` 至 `1000` 的范围内;
- 操作数将在 `1` 至 `1000` 的范围内;
- 请不要使用内置的队列库。
#### 💎 代码
```javascript
/**
* @param {number} k
*/
var MyCircularQueue = function (k) {
this.queue = new Array(k);
this.head = 0;
this.tail = 0;
this.size = k;
};
/**
* @param {number} value
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.enQueue = function (value) {
if (this.isFull()) return false;
this.queue[this.tail] = value;
// 将 tail 指向队尾的下一个空间
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % this.size;
return true;
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.deQueue = function () {
if (this.isEmpty()) return false;
this.queue[this.head] = null;
// 将 head 指向新的队头
this.head = (this.head + 1) % this.size;
return true;
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Front = function () {
return this.isEmpty() ? -1 : this.queue[this.head];
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.Rear = function () {
// 因为 tail 指向队尾的下一个空间,所以要分情况处理
// 若 tail == 0,那队尾应该在 size - 1
// 其他情况,队尾在 tail - 1
let index = this.tail === 0 ? this.size - 1 : this.tail - 1;
return this.isEmpty() ? -1 : this.queue[index];
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isEmpty = function () {
// head == tail 时,有两种情况
// 一种是队列为空,此时 queue[head] 为null
// 一种是队列满了,此时 queue[head] 有值
return this.head === this.tail && !this.queue[this.head];
};
/**
* @return {boolean}
*/
MyCircularQueue.prototype.isFull = function () {
return this.head === this.tail && !!this.queue[this.head];
};
```
优先队列
定义
优先队列(Priority Queue) :一种特殊的队列。在优先队列中,元素被赋予优先级,当访问队列元素时,具有最高优先级的元素最先删除。
优先队列与普通队列最大的不同点在于 出队顺序。
- 普通队列的出队顺序跟入队顺序相关,符合 先进先出(First in, First out) 的规则;
- 优先队列的出队顺序跟入队顺序无关,优先队列是按照元素的优先级来决定出队顺序的。优先级高的元素优先出队,优先级低的元素后出队。优先队列符合 最高级先出(First in, Largest out) 的规则;
优先队列的实现方式有很多种,除了使用 数组 实现(顺序存储)与 链表 实现(链式存储)之外,最常用的是使用 二叉堆 实现。
数组实现
数组按优先级升序排序( priority 值越小,优先级越高),入队需要遍历整个数组,插入到合适的位置,时间复杂度为 O(n)。出队直接返回队头元素,并删除队头元素,时间复杂度为 O(1);
// 优先队列内部的元素类
class QueueElement {
constructor(data, priority) {
this.data = data;
this.priority = priority;
}
}
// 优先队列类(继承 ArrayQueue 类)
class PriorityQueue extends ArrayQueue {
constructor() {
super();
}
// 入队,将元素按优先级加入到队列中
// 重写 enQueue()
enQueue(data, priority) {
// 根据传入的元素,创建 QueueElement 对象
const queueElement = new QueueElement(data, priority);
// 判断队列是否为空
if (this.isEmpty()) {
// 如果为空,不用判断优先级,直接添加
this._queue.push(queueElement);
} else {
// 定义一个变量记录是否成功添加了新元素
let added = false;
for (let i = 0; i < this._queue.length; i++) {
// 让新插入的元素进行优先级比较,priority 值越小,优先级越大
if (queueElement.priority < this._queue[i].priority) {
// 在指定的位置插入元素
this._queue.splice(i, 0, queueElement);
added = true;
break;
}
}
// 如果遍历完所有元素,优先级都大于新插入的元素,就将新插入的元素插入到最后
if (!added) {
this._queue.push(queueElement);
}
}
}
// 将队列中元素以字符串形式返回
// 重写 toString()
toString() {
let res = [];
for (let item of this._queue) {
res.push(item.data + '-' + item.priority);
}
return res.join(',');
}
// 其他属性继承 ArrayQueue 类的
}
👉 查看代码测试 👈
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
priorityQueue.enQueue('A', 10);
priorityQueue.enQueue('B', 15);
priorityQueue.enQueue('C', 11);
priorityQueue.enQueue('D', 20);
priorityQueue.enQueue('E', 18);
priorityQueue.print();
// output:
// [QueueElement {data: 'A', priority: 10},
// QueueElement {data: 'C', priority: 11},
// QueueElement {data: 'B', priority: 15},
// QueueElement {data: 'E', priority: 18},
// QueueElement {data: 'D', priority: 20}]
priorityQueue.deQueue();
priorityQueue.deQueue();
priorityQueue.print();
// output:
// [QueueElement {data: 'B', priority: 15},
// QueueElement {data: 'E', priority: 18},
// QueueElement {data: 'D', priority: 20}]
console.log(priorityQueue.isEmpty()); // output: false
console.log(priorityQueue.count()); // output: 3
console.log(priorityQueue.toString()); // output: B-15,E-18,D-20
链表实现
链表中的元素按照优先级排序,入队操作需要为待插入元素创建节点,并在链表中找到合适的插入位置,时间复杂度为 O(n)。出队操作直接返回链表队头元素,并删除队头元素,时间复杂度为 O(1);
class Node {
constructor(data, priority) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.priority = priority;
}
}
// 优先队列类(继承 LinkedListQueue 类)
class PriorityQueue extends LinkedListQueue {
constructor() {
super();
}
// 入队,将元素按优先级加入到队列中
// 重写 enQueue()
enQueue(data, priority) {
const node = new Node(data, priority);
if (this.isEmpty()) {
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
} else {
let prev = new Node(0, 0);
prev.next = this.head;
// 定义一个变量记录是否成功添加了新元素
let added = false;
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (node.priority < prev.next.priority && !added) {
let temp = prev.next;
prev.next = node;
node.next = temp;
prev = node;
added = true;
}
prev = prev.next;
this.tail = prev;
}
// 如果遍历完所有元素,优先级都大于新插入的元素,就将新插入的元素插入到最后
if (!added) {
this.tail.next = node;
this.tail = this.tail.next;
}
}
this.length++;
}
// 将队列中元素以字符串形式返回
toString() {
let res = [];
let prev = this.head;
while (prev) {
res.push(prev.data + '-' + prev.priority);
prev = prev.next;
}
return res.join(',');
}
// 其他属性都继承 LinkedListQueue 类
}
👉 查看代码测试 👈
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
priorityQueue.enQueue('A', 10);
priorityQueue.enQueue('B', 15);
priorityQueue.enQueue('C', 11);
priorityQueue.enQueue('D', 20);
priorityQueue.enQueue('E', 18);
priorityQueue.print();
// output:
// Node {data: 'A', priority: 10, next: Node {
// data: 'C', priority: 11, next: Node {
// data: 'B', priority: 15, next: Node {
// data: 'E', priority: 18, next: Node {
// data: 'D', priority: 20, next: null }}}}}
priorityQueue.deQueue();
priorityQueue.deQueue();
priorityQueue.print();
// output:
// Node {data: 'B', priority: 15, next: Node {
// data: 'E', priority: 18, next: Node {
// data: 'D', priority: 20, next: null }}}
console.log(priorityQueue.isEmpty()); // output: false
console.log(priorityQueue.count()); // output: 3
console.log(priorityQueue.toString()); // output: B-15,E-18,D-20
二叉堆实现
堆是一种特殊的二叉树,关于堆的知识点,可以详见:2.7 堆。
Java 中的优先队列就是基于堆实现的,是一个小顶堆。往优先队列中插入一个元素,就相当于往堆中插入一个元素;从优先队列中取出优先级最高的元素,就相当于取出堆顶元素。
构建一个二叉堆结构,二叉堆按照优先级进行排序。入队操作就是将元素插入到二叉堆中合适位置,时间复杂度为 O(logn)。出队操作则返回二叉堆中优先级最大节点并删除,时间复杂度也是 O(logn);
class PriorityQueue extends ArrayQueue {
constructor() {
super();
}
enQueue(data, priority) {
const queueElement = new QueueElement(data, priority);
this._queue.push(queueElement);
this._heapifyUp();
}
deQueue() {
if (this._queue.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const highestPriority = this._queue[0];
const last = this._queue.pop();
if (this._queue.length > 0) {
this._queue[0] = last;
this._heapifyDown(0);
}
return highestPriority;
}
_heapifyUp() {
let cur = this._queue.length - 1;
while (cur > 0) {
const parent = Math.floor((cur - 1) / 2);
if (this._queue[cur].priority > this._queue[parent].priority) {
[this._queue[cur], this._queue[parent]] = [
this._queue[parent],
this._queue[cur]
];
cur = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
_heapifyDown(index) {
let cur = 0;
while (true) {
const leftChild = 2 * cur + 1;
const rightChild = 2 * cur + 2;
let next = null;
if (
leftChild < this._queue.length &&
this._queue[leftChild].priority > this._queue[cur].priority
) {
next = leftChild;
}
if (
rightChild < this._queue.length &&
this._queue[rightChild].priority > this._queue[cur].priority
) {
next =
this._queue[rightChild].priority > this._queue[leftChild].priority
? rightChild
: leftChild;
}
if (
next !== null &&
this._queue[cur].priority < this._queue[next].priority
) {
[this._queue[cur], this._queue[next]] = [
this._queue[next],
this._queue[cur]
];
cur = next;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
// 将队列中元素以字符串形式返回
// 重写 toString()
toString() {
let res = [];
for (let item of this._queue) {
res.push(item.data + '-' + item.priority);
}
return res.join(',');
}
// 其他属性都继承 ArrayQueue 类
}
👉 查看代码测试 👈
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
priorityQueue.enQueue('A', 10);
priorityQueue.enQueue('B', 15);
priorityQueue.enQueue('C', 11);
priorityQueue.enQueue('D', 20);
priorityQueue.enQueue('E', 18);
priorityQueue.toString();
// output: 'D-20,E-18,C-11,A-10,B-15'
priorityQueue.deQueue();
priorityQueue.deQueue();
priorityQueue.toString();
// output: 'B-15,A-10,C-11'
console.log(priorityQueue.isEmpty()); // output: false
console.log(priorityQueue.count()); // output: 3
时间复杂度
三种结构实现的优先队列,入队操作和出队操作的时间复杂度总结:
| 时间复杂度 | 入队 | 出队 |
|---|---|---|
| 数组 | O(n) | O(1) |
| 链表 | O(n) | O(1) |
| 二叉堆 | O(logn) | O(logn) |
优先队列的应用
优先队列的应用场景非常多,比如:
- 数据压缩:赫夫曼编码算法;
- 最短路径算法:Dijkstra 算法;
- 最小生成树算法:Prim 算法;
- 任务调度器:根据优先级执行系统任务;
- 事件驱动仿真:顾客排队算法;
- 排序问题:查找第 k 个最小元素;
相关题目
队列基础题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 622 | 设计循环队列 | [✓] | 设计 队列 数组 1+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 346 | 数据流中的移动平均值 🔒 | [✓] | 设计 队列 数组 1+ | 🟢 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 225 | 用队列实现栈 | [✓] | 栈 设计 队列 | 🟢 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
优先队列
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 703 | 数据流中的第 K 大元素 | [✓] | 树 设计 二叉搜索树 3+ | 🟢 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 347 | 前 K 个高频元素 | [✓] | 数组 哈希表 分治 5+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 451 | 根据字符出现频率排序 | [✓] | 哈希表 字符串 桶排序 3+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 973 | 最接近原点的 K 个点 | [✓] | 几何 数组 数学 4+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 1296 | 划分数组为连续数字的集合 | 贪心 数组 哈希表 1+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 239 | 滑动窗口最大值 | [✓] | 队列 数组 滑动窗口 2+ | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 295 | 数据流的中位数 | [✓] | 设计 双指针 数据流 2+ | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 23 | 合并 K 个升序链表 | [✓] | 链表 分治 堆(优先队列) 1+ | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 218 | 天际线问题 | 树状数组 线段树 数组 4+ | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
