2.7 堆
2.7 堆
堆的定义
定义
堆(Heap) 是一种特殊的树形数据结构,只要满足以下两点的树,就是堆:
- 堆是一个完全二叉树;
- 堆中每一个节点的值都必须大于等于(或小于等于)其子树中每个节点的值。
对于每个节点的值都大于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,叫作 大顶堆 。对于每个节点的值都小于等于子树中每个节点值的堆,叫作 小顶堆 。
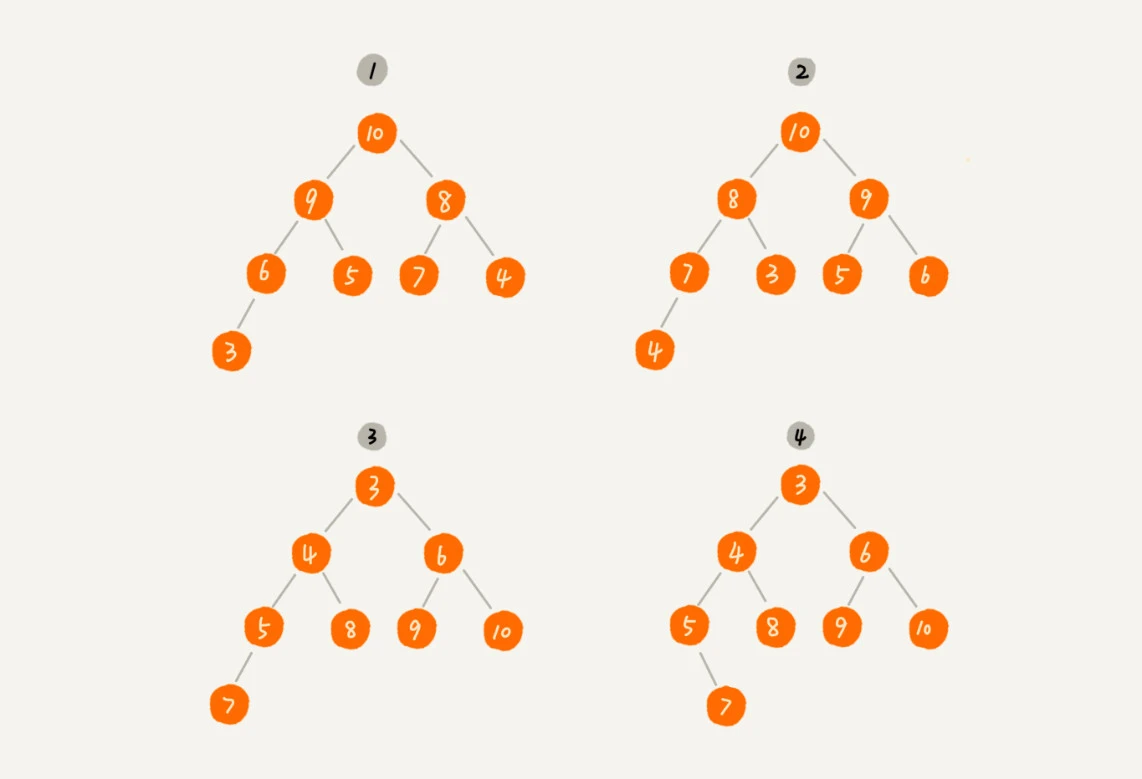
如图所示,第 1 个和第 2 个是大顶堆,第 3 个是小顶堆,第 4 个不是堆。
堆的实现
堆是一个完全二叉树,完全二叉树比较适合用数组来存储。
用数组来存储完全二叉树是非常节省存储空间的,因为不需要存储左右子节点的指针,单纯地通过数组的下标,就可以找到一个节点的左右子节点和父节点。
比如大顶堆:
7
/ \
5 6
/ \ \
4 2 1
可以储存为数组:[7, 5, 6, 4, 2, 1],数组中下标为 i 的节点的左子节点,就是下标为 i * 2 + 1 的节点,右子节点就是下标为 i * 2 + 2 的节点,父节点就是下标为 Math.floor((i - 1) / 2) 的节点。
知道了如何存储一个堆,再来看看堆上有哪些操作。
1. 插入操作
插入操作是指将元素添加到堆中,并保持堆的性质。通常是将元素添加到数组的末尾,然后执行一系列比较操作,让其重新满足堆的特性,这个过程就叫做 堆化(heapify) 。
堆化实际上有两种,从下往上和从上往下。这里以从下往上的堆化方法为例。
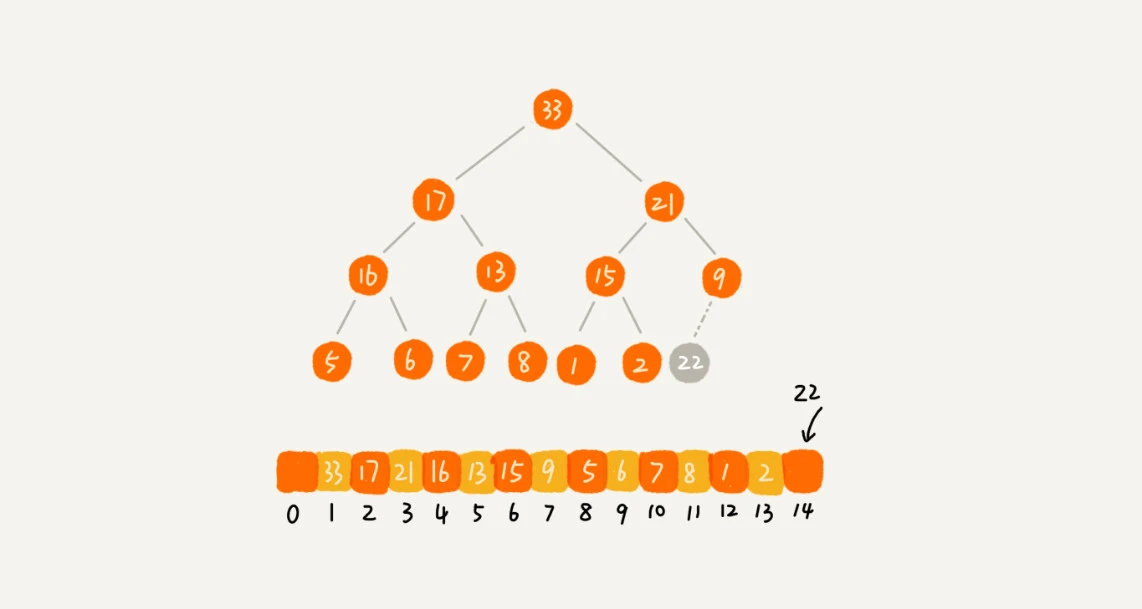
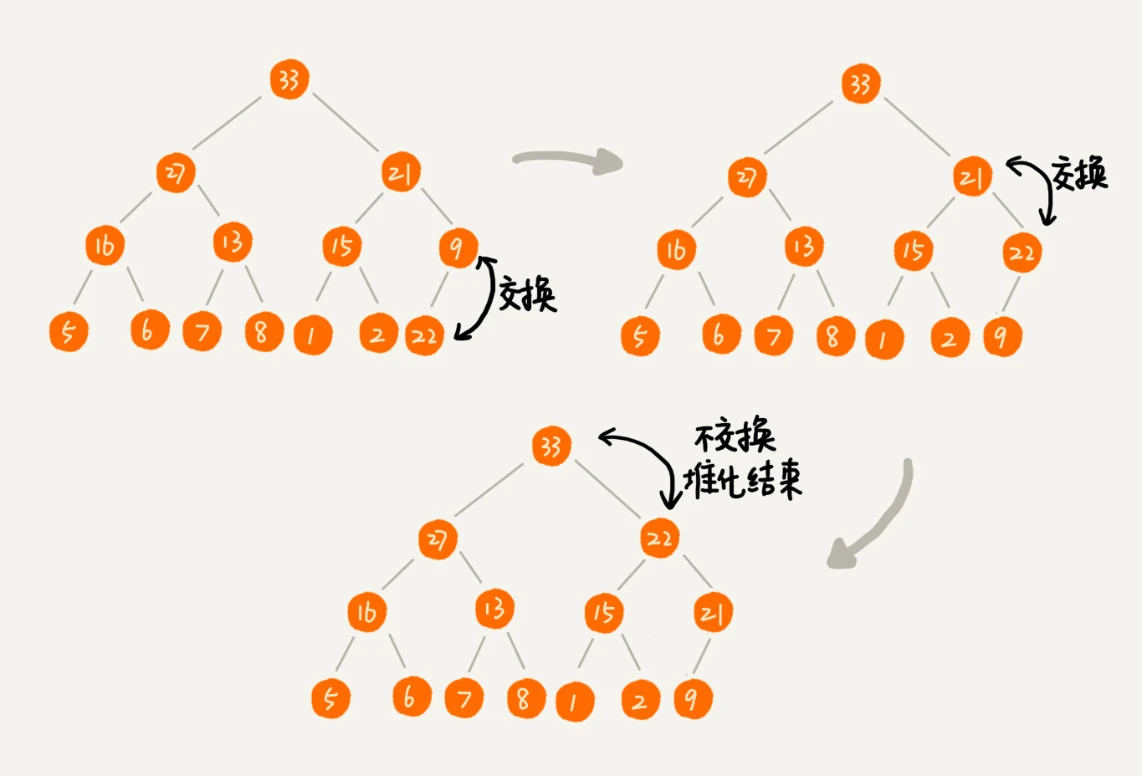
可以让新插入的节点与父节点对比大小,如果不满足子节点小于等于父节点的大小关系,就互换两个节点。一直重复这个过程,直到父子节点之间满足刚说的那种大小关系。
insert 函数代码如下:
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
this._heapifyUp();
}
_heapifyUp() {
let cur = this.heap.length - 1;
while (cur > 0) {
const parent = Math.floor((cur - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[cur] > this.heap[parent]) {
[this.heap[cur], this.heap[parent]] = [
this.heap[parent],
this.heap[cur]
];
cur = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
// Example usage
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
maxHeap.insert(5);
maxHeap.insert(10);
maxHeap.insert(3);
console.log(maxHeap.heap); // Output: [10, 5, 3]
2. 删除操作
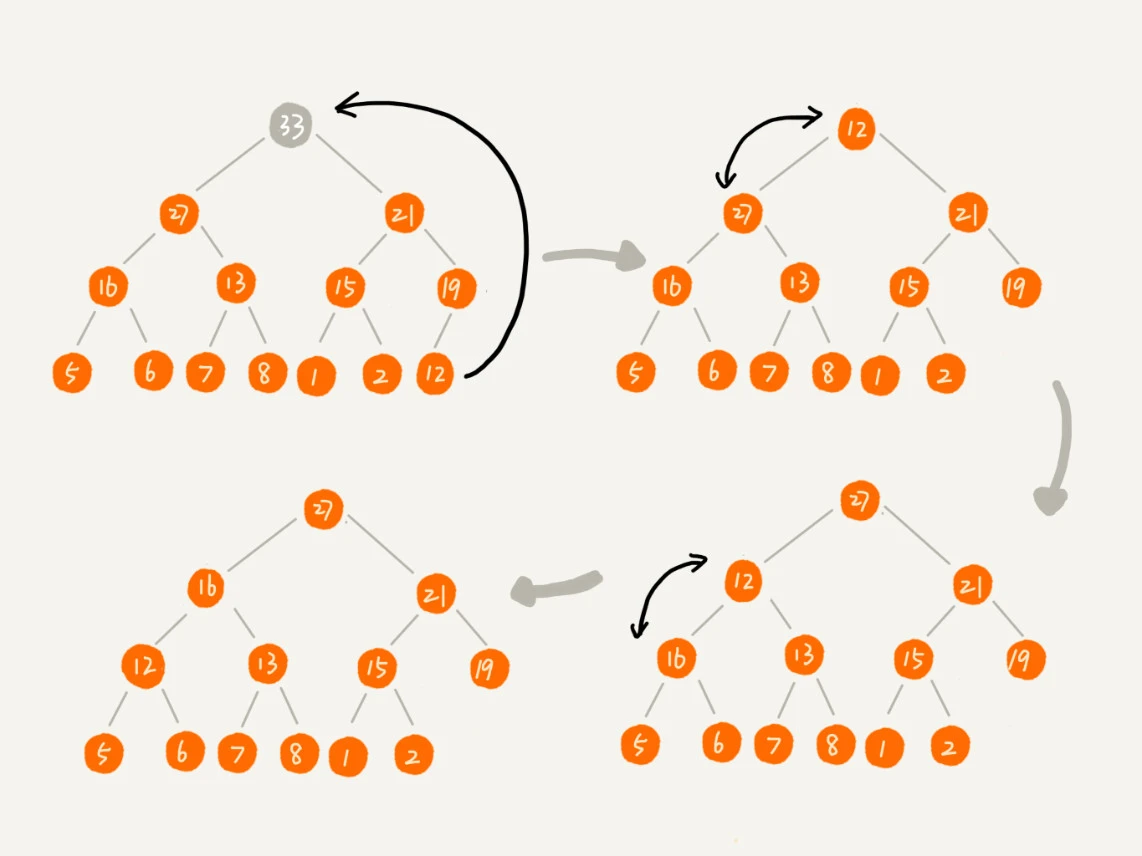
删除操作是指从堆中移除元素,并保持堆的性质。通常是将根节点删除,然后将最后一个节点移到根的位置,并根据堆的性质进行调整。
从堆的定义的第二条中,任何节点的值都大于等于(或小于等于)子树节点的值,可以发现,堆顶元素存储的就是堆中数据的最大值或者最小值。
假设构造的是大顶堆,堆顶元素就是最大的元素。当删除堆顶元素之后,就需要把第二大的元素放到堆顶,然后再迭代地删除第二大节点,以此类推,直到叶子节点被删除。
不过这种方法有点问题,就是最后堆化出来的堆并不满足完全二叉树的特性,会出现数组空洞。
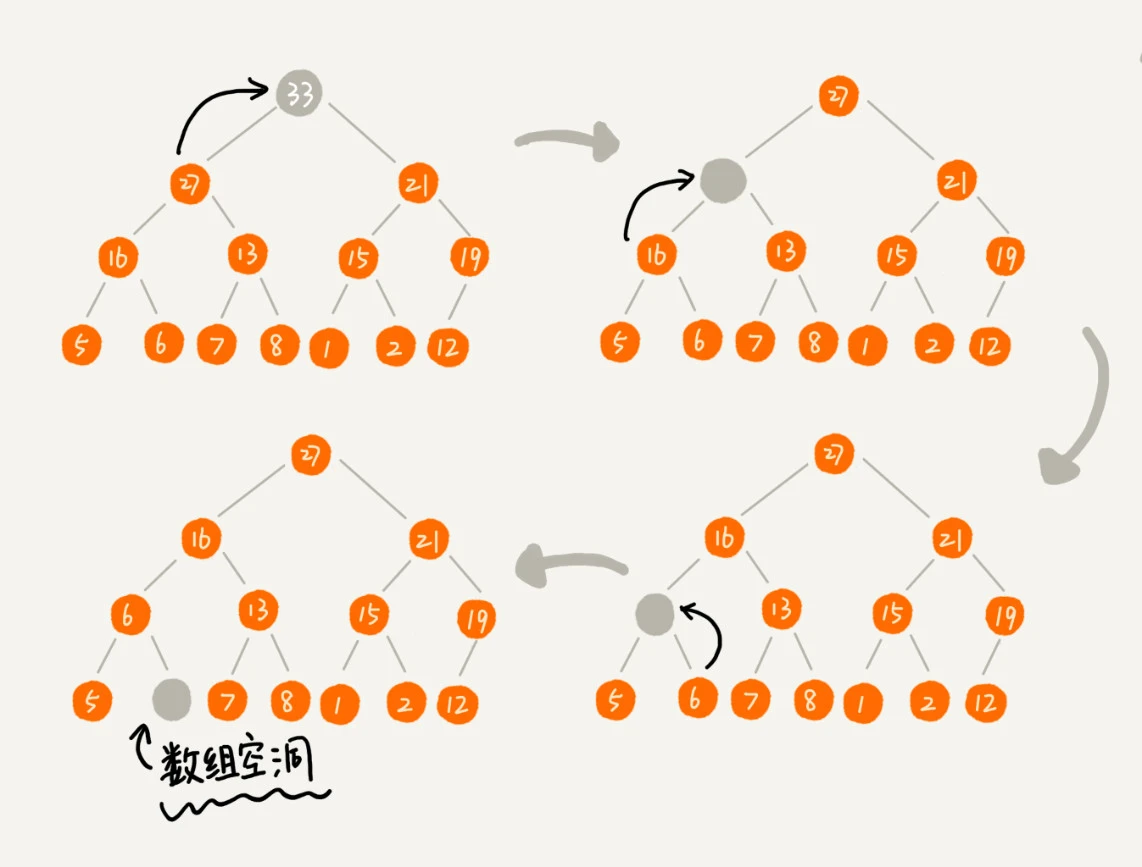
稍微改变一下思路,可以把最后一个节点放到堆顶,然后利用同样的父子节点对比方法。对于不满足父子节点大小关系的,互换两个节点,并且重复进行这个过程,直到父子节点之间满足大小关系为止。这就是从上往下的堆化方法。
因为移除的是数组中的最后一个元素,而堆化的过程中都是交换操作,不会出现数组中的“空洞”,所以这种方法堆化之后的结果,肯定满足完全二叉树的特性。
class MaxHeap {
// ...(之前的代码)
extractMax() {
if (this.heap.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const max = this.heap[0];
const last = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = last;
this._heapifyDown();
}
return max;
}
_heapifyDown() {
let cur = 0;
while (true) {
const leftChild = 2 * cur + 1;
const rightChild = 2 * cur + 2;
let next = null;
if (
leftChild < this.heap.length &&
this.heap[leftChild] > this.heap[cur]
) {
next = leftChild;
}
if (
rightChild < this.heap.length &&
this.heap[rightChild] > this.heap[cur]
) {
next =
this.heap[rightChild] > this.heap[leftChild] ? rightChild : leftChild;
}
if (next !== null && this.heap[cur] < this.heap[next]) {
[this.heap[cur], this.heap[next]] = [this.heap[next], this.heap[cur]];
cur = next;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
// Example usage
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
maxHeap.insert(5);
maxHeap.insert(10);
maxHeap.insert(3);
console.log(maxHeap.extractMax()); // Output: 10
console.log(maxHeap.heap); // Output: [5, 3]
3. 堆化操作
堆化操作是指将一个无序的数组(或者部分数组)调整为堆的过程。通常有两种堆化操作:自顶向下的堆化和自底向上的堆化。
以自底向上的堆化过程为例:
先计算出最后一个非叶子节点的索引 lastNonLeaf 。在一个堆中,最后一个非叶子节点的索引可以通过 (n-2) / 2 计算得到,其中 n 是堆中元素的个数。
然后从最后一个非叶子节点 lastNonLeaf 开始,逐个向前遍历所有的非叶子节点,对每个节点执行自底向上的堆化操作。
class MaxHeap {
// ...(之前的代码)
buildHeap(arr) {
this.heap = arr;
const lastNonLeaf = Math.floor((this.heap.length - 2) / 2);
for (let i = lastNonLeaf; i >= 0; i--) {
this._heapifyDown(i);
}
}
}
// Example usage
const maxHeap = new MaxHeap();
maxHeap.buildHeap([8, 4, 10, 3, 5]);
console.log(maxHeap.heap); // Output: [10, 5, 8, 3, 4]
堆的应用
堆作为一种数据结构,有着广泛的应用,其中包括但不限于以下情景:
- 堆排序:基于堆实现的一种排序算法。
- 优先队列:基于堆实现的一种数据结构,能够快速访问最大(或最小)值。
- Dijkstra 算法:用于计算最短路径的图算法中使用了优先队列,通常基于堆实现。
- 操作系统调度:一些操作系统中使用堆来管理进程或任务的优先级。
堆排序
堆排序是一种基于堆的排序算法,它利用堆的性质进行排序。堆排序分为两个阶段:建堆和排序。
1. 建堆
在建堆阶段,将数组视为一个完全二叉树,然后从最后一个非叶子节点开始,依次对每个节点进行堆化操作,使得整个数组满足堆的性质。
function buildHeap(arr) {
const lastNonLeaf = Math.floor((arr.length - 2) / 2);
for (let i = lastNonLeaf; i >= 0; i--) {
heapifyDown(arr, i, arr.length);
}
}
// Example usage
const arrayToSort = [8, 4, 10, 3, 5];
buildHeap(arrayToSort);
console.log(arrayToSort); // Output: [10, 5, 8, 3, 4]
2. 排序
在建堆完成后,最大(或最小)元素已经位于堆的根节点。
以大顶堆为例,数组中的第一个元素就是堆顶,也就是最大的元素。把它跟最后一个元素交换,那最大元素就放到了下标为 n 的位置。
这个过程有点类似上面讲的“删除堆顶元素”的操作,当堆顶元素移除之后,把下标为 n 的元素放到堆顶,然后再通过堆化的方法,将剩下的 n-1 个元素重新构建成堆。堆化完成之后,再取堆顶的元素,放到下标是 n-1 的位置,一直重复这个过程,直到最后堆中只剩下标为 1 的一个元素,排序工作就完成了。

function heapSort(arr) {
buildHeap(arr);
for (let i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
[arr[0], arr[i]] = [arr[i], arr[0]];
heapifyDown(arr, 0, i);
}
}
// Example usage
const arrayToSort = [8, 4, 10, 3, 5];
heapSort(arrayToSort);
console.log(arrayToSort); // Output: [3, 4, 5, 8, 10]
堆排序包括建堆和排序两个操作,建堆过程的时间复杂度是 O(n) ,排序过程的时间复杂度是 O(nlog n) ,所以,堆排序整体的时间复杂度是 O(nlog n) 。
优先队列
优先队列是一种支持按优先级顺序访问元素的数据结构。基于堆实现的优先队列可以在 O(log n) 的时间内找到并删除具有最高(或最低)优先级的元素。
class PriorityQueue {
constructor() {
this.heap = [];
}
enqueue(item) {
this.heap.push(item);
this._heapifyUp();
}
dequeue() {
if (this.heap.length === 0) {
return null;
}
const highestPriority = this.heap[0];
const last = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = last;
this._heapifyDown(0);
}
return highestPriority;
}
_heapifyUp() {
// Similar to the previous MaxHeap example
// ...
}
_heapifyDown(index) {
// Similar to the previous MaxHeap example
// ...
}
}
// Example usage
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
priorityQueue.enqueue({ value: 'Task A', priority: 2 });
priorityQueue.enqueue({ value: 'Task B', priority: 1 });
priorityQueue.enqueue({ value: 'Task C', priority: 3 });
console.log(priorityQueue.dequeue()); // Output: { value: "Task C", priority: 3 }
console.log(priorityQueue.dequeue()); // Output: { value: "Task A", priority: 2 }
TOP K 问题
求 Top K 问题分为两类:一类是针对静态数据集合,数据集合事先确定,不会再变;另一类是针对动态数据集合,数据集合事先并不确定,有数据动态地加入到集合中。
静态数组
针对静态数据,想要在一个包含 n 个数据的数组中,查找前 K 大的数据,可以维护一个大小为 K 的小顶堆:
- 顺序遍历数组,从数组中取出取数据与堆顶元素比较;
- 如果比堆顶元素大,就把堆顶元素删除,并且将这个元素插入到堆中;
- 如果比堆顶元素小,则不做处理,继续遍历数组;
- 遍历完数组中的数据之后,堆中的数据就是前
K大数据;
遍历数组需要 O(n) 的时间复杂度,一次堆化操作需要 O(logK) 的时间复杂度,所以最坏情况下,n 个元素都入堆一次,所以时间复杂度就是 O(nlogK) 。
动态数组
针对动态数据求得 Top K 就是实时 Top K。
假设数组在不断插入数据,如果每次求前 K 大的数据,都基于当前的数据重新计算的话,那时间复杂度就是 O(nlogK),n 表示当前的数据的大小。
实际上,可以维护一个 K 大小的小顶堆,当有数据被添加到数组中时,就拿它与堆顶的元素对比。
- 如果比堆顶元素大,就把堆顶元素删除,并且将这个元素插入到堆中;
- 如果比堆顶元素小,则不做处理;
这样,无论任何时候需要查询当前的前 K 大的数据,都可以立刻返回。
对于插入操作,最坏情况下,我们需要进行堆化的次数是堆的高度,即 log K。因此,插入操作的时间复杂度是 O(log K)。在初始化时,需要将前 K 个元素构建最小堆,这一过程的时间复杂度是 O(Klog K)。总体来说,时间复杂度主要受插入操作的影响,为 O(log K)。
📌 703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素 - LeetCode
💻 题目大意
设计一个找到数据流中第 k 大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第 k 大元素,不是第 k 个不同的元素。
请实现 KthLargest 类:
KthLargest(int k, int[] nums)使用整数k和整数流nums初始化对象。int add(int val)将val插入数据流nums后,返回当前数据流中第k大的元素
💡 解题思路
动态数组求 Top K 问题,使用大小为 K 的小顶堆。
💎 代码
class KthLargest {
// @param {number} k
// @param {number[]} nums
constructor(k, nums) {
this.k = k;
this.heap = [];
for (let i of nums) {
this.add(i);
}
}
// @param {number} val
// @return {number}
add(val) {
if (this.heap.length < this.k) {
this.heap.push(val);
this.heapifyUp(this.heap.length - 1);
} else if (this.heap[0] < val) {
this.heap[0] = val;
this.heapifyDown(0);
}
return this.heap[0];
}
heapifyUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parent = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[parent] > this.heap[index]) {
[this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]] = [
this.heap[index],
this.heap[parent]
];
index = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
heapifyDown(index) {
const left = 2 * index + 1;
const right = 2 * index + 2;
let min = index;
if (left < this.heap.length && this.heap[left] < this.heap[min]) {
min = left;
}
if (right < this.heap.length && this.heap[right] < this.heap[min]) {
min = right;
}
if (min !== index) {
[this.heap[min], this.heap[index]] = [this.heap[index], this.heap[min]];
this.heapifyDown(min);
}
}
}
#### 📌 [703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素 - LeetCode](https://leetcode.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-a-stream/)
#### 💻 **题目大意**
设计一个找到数据流中第 `k` 大元素的类(class)。注意是排序后的第 `k` 大元素,不是第 `k` 个不同的元素。
请实现 `KthLargest` 类:
- `KthLargest(int k, int[] nums)` 使用整数 `k` 和整数流 `nums` 初始化对象。
- `int add(int val)` 将 `val` 插入数据流 `nums` 后,返回当前数据流中第 `k` 大的元素
#### 💡 **解题思路**
动态数组求 Top K 问题,使用大小为 K 的小顶堆。
#### 💎 **代码**
```javascript
class KthLargest {
// @param {number} k
// @param {number[]} nums
constructor(k, nums) {
this.k = k;
this.heap = [];
for (let i of nums) {
this.add(i);
}
}
// @param {number} val
// @return {number}
add(val) {
if (this.heap.length < this.k) {
this.heap.push(val);
this.heapifyUp(this.heap.length - 1);
} else if (this.heap[0] < val) {
this.heap[0] = val;
this.heapifyDown(0);
}
return this.heap[0];
}
heapifyUp(index) {
while (index > 0) {
const parent = Math.floor((index - 1) / 2);
if (this.heap[parent] > this.heap[index]) {
[this.heap[parent], this.heap[index]] = [
this.heap[index],
this.heap[parent]
];
index = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
heapifyDown(index) {
const left = 2 * index + 1;
const right = 2 * index + 2;
let min = index;
if (left < this.heap.length && this.heap[left] < this.heap[min]) {
min = left;
}
if (right < this.heap.length && this.heap[right] < this.heap[min]) {
min = right;
}
if (min !== index) {
[this.heap[min], this.heap[index]] = [this.heap[index], this.heap[min]];
this.heapifyDown(min);
}
}
}
```
求中位数
📌 295. 数据流的中位数 - LeetCode
💻 题目大意
中位数是有序整数列表中的中间值。如果列表的大小是偶数,则没有中间值,中位数是两个中间值的平均值。
- 例如
arr = [2,3,4]的中位数是3。 - 例如
arr = [2,3]的中位数是(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5。
实现 MedianFinder 类:
MedianFinder()初始化MedianFinder对象。void addNum(int num)将数据流中的整数num添加到数据结构中。double findMedian()返回到目前为止所有元素的中位数。与实际答案相差10^-5以内的答案将被接受。
💡 解题思路
可以使用两个堆来解决问题。
- 初始化一个小顶堆
small和一个大顶堆large来存储数据; - 求中位数:
- 当两个堆的长度一样时,两个堆顶的平均数就是中位数;
- 当两个堆的长度不一样时,更长的那个堆的堆顶就是中位数;
- 添加数据:
- 如果小顶堆
small的数据比大顶堆large的数据多,那么将数据添加到small中,再将small的堆顶(也即最小值)推出,推入到large中,如此便可以保证small中的数据都大于large中的数; - 反之,如果小顶堆
small的数据比大顶堆large的数据少,那么将数据添加到large中,再将large的堆顶(也即最大值)推出,推入到small中,如此便可以保证small中的数据都大于large中的数;
- 如果小顶堆
💎 代码
var MedianFinder = function () {
// 小顶堆
this.small = new MinPriorityQueue();
// 大顶堆
this.large = new MaxPriorityQueue();
};
/**
* @param {number} num
* @return {void}
*/
MedianFinder.prototype.addNum = function (num) {
if (this.small.size() >= this.large.size()) {
this.small.insert(num);
this.large.insert(this.small.pop());
} else {
this.large.insert(num);
this.small.insert(this.large.pop());
}
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MedianFinder.prototype.findMedian = function () {
const lenSmall = this.small.size(),
lenLarge = this.large.size();
// 如果元素不一样多,多的那个堆的堆顶元素就是中位数
if (lenSmall > lenLarge) {
return this.small.heap[0];
} else if (lenSmall < lenLarge) {
return this.large.heap[0];
}
// 如果元素一样多,两个堆堆顶元素的平均数是中位数
return (this.small.heap[0] + this.large.heap[0]) / 2;
};
class MaxPriorityQueue {
// ...
}
class MinPriorityQueue {
// ...
}
#### 📌 [295. 数据流的中位数 - LeetCode](https://leetcode.com/problems/find-median-from-data-stream/)
#### 💻 **题目大意**
中位数是有序整数列表中的中间值。如果列表的大小是偶数,则没有中间值,中位数是两个中间值的平均值。
- 例如 `arr = [2,3,4]` 的中位数是 `3` 。
- 例如 `arr = [2,3]` 的中位数是 `(2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5` 。
实现 `MedianFinder` 类:
- `MedianFinder()` 初始化 `MedianFinder` 对象。
- `void addNum(int num)` 将数据流中的整数 `num` 添加到数据结构中。
- `double findMedian()` 返回到目前为止所有元素的中位数。与实际答案相差 `10^-5` 以内的答案将被接受。
#### 💡 **解题思路**
可以使用两个堆来解决问题。
- 初始化一个小顶堆 `small` 和一个大顶堆 `large` 来存储数据;
- 求中位数:
- 当两个堆的长度一样时,两个堆顶的平均数就是中位数;
- 当两个堆的长度不一样时,更长的那个堆的堆顶就是中位数;
- 添加数据:
- 如果小顶堆 `small` 的数据比大顶堆 `large` 的数据多,那么将数据添加到 `small` 中,再将 `small` 的堆顶(也即最小值)推出,推入到 `large` 中,如此便可以保证 `small` 中的数据都大于 `large` 中的数;
- 反之,如果小顶堆 `small` 的数据比大顶堆 `large` 的数据少,那么将数据添加到 `large` 中,再将 `large` 的堆顶(也即最大值)推出,推入到 `small` 中,如此便可以保证 `small` 中的数据都大于 `large` 中的数;
#### 💎 **代码**
```javascript
var MedianFinder = function () {
// 小顶堆
this.small = new MinPriorityQueue();
// 大顶堆
this.large = new MaxPriorityQueue();
};
/**
* @param {number} num
* @return {void}
*/
MedianFinder.prototype.addNum = function (num) {
if (this.small.size() >= this.large.size()) {
this.small.insert(num);
this.large.insert(this.small.pop());
} else {
this.large.insert(num);
this.small.insert(this.large.pop());
}
};
/**
* @return {number}
*/
MedianFinder.prototype.findMedian = function () {
const lenSmall = this.small.size(),
lenLarge = this.large.size();
// 如果元素不一样多,多的那个堆的堆顶元素就是中位数
if (lenSmall > lenLarge) {
return this.small.heap[0];
} else if (lenSmall < lenLarge) {
return this.large.heap[0];
}
// 如果元素一样多,两个堆堆顶元素的平均数是中位数
return (this.small.heap[0] + this.large.heap[0]) / 2;
};
class MaxPriorityQueue {
// ...
}
class MinPriorityQueue {
// ...
}
```
Dijkstra 算法
Dijkstra 算法是一种用于计算图中最短路径的贪心算法。在算法的实现中,使用了基于最小堆的优先队列来高效地选择下一个要探索的节点。
function dijkstra(graph, start) {
const distances = {};
const priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
// Initialize distances and enqueue the start node
for (const vertex in graph) {
distances[vertex] = Infinity;
}
distances[start] = 0;
priorityQueue.enqueue({ node: start, distance: 0 });
while (priorityQueue.heap.length > 0) {
const { node, distance } = priorityQueue.dequeue();
if (distance > distances[node]) {
continue;
}
for (const neighbor in graph[node]) {
const newDistance = distance + graph[node][neighbor];
if (newDistance < distances[neighbor]) {
distances[neighbor] = newDistance;
priorityQueue.enqueue({ node: neighbor, distance: newDistance });
}
}
}
return distances;
}
// Example usage
const weightedGraph = {
A: { B: 1, C: 4 },
B: { A: 1, C: 2, D: 5 },
C: { A: 4, B: 2, D: 1 },
D: { B: 5, C: 1 }
};
console.log(dijkstra(weightedGraph, 'A'));
// Output: { A: 0, B: 1, C: 3, D: 4 }
操作系统调度
在操作系统中,任务调度是一个重要的问题。通过使用基于堆的数据结构,可以轻松地管理和调度任务的优先级。
