388. 文件的最长绝对路径
388. 文件的最长绝对路径
🟠 🔖 栈 深度优先搜索 字符串 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
Suppose we have a file system that stores both files and directories. An example of one system is represented in the following picture:
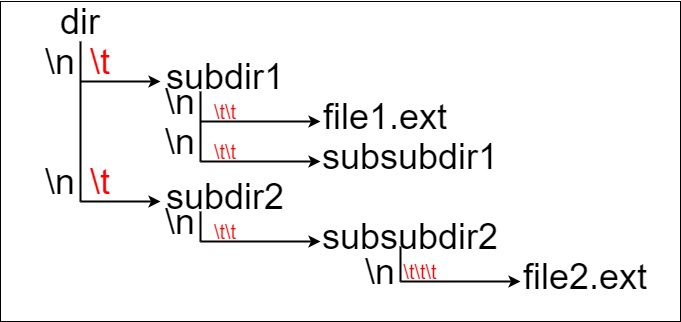
Here, we have dir as the only directory in the root. dir contains two subdirectories, subdir1 and subdir2. subdir1 contains a file file1.ext and subdirectory subsubdir1. subdir2 contains a subdirectory subsubdir2, which contains a file file2.ext.
In text form, it looks like this (with ⟶ representing the tab character):
dir
⟶ subdir1
⟶ ⟶ file1.ext
⟶ ⟶ subsubdir1
⟶ subdir2
⟶ ⟶ subsubdir2
⟶ ⟶ ⟶ file2.ext
If we were to write this representation in code, it will look like this: "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext". Note that the '\n' and '\t' are the new-line and tab characters.
Every file and directory has a unique absolute path in the file system, which is the order of directories that must be opened to reach the file/directory itself, all concatenated by '/'s. Using the above example, the absolute path to file2.ext is "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext". Each directory name consists of letters, digits, and/or spaces. Each file name is of the form name.extension, where name and extension consist of letters, digits, and/or spaces.
Given a string input representing the file system in the explained format, return the length of thelongest absolute path to a file in the abstracted file system. If there is no file in the system, return 0.
Note that the testcases are generated such that the file system is valid and no file or directory name has length 0.
Example 1:
Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext"
Output: 20
Explanation: We have only one file, and the absolute path is "dir/subdir2/file.ext" of length 20.
Example 2:
Input: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext"
Output: 32
Explanation: We have two files:
"dir/subdir1/file1.ext" of length 21
"dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" of length 32.
We return 32 since it is the longest absolute path to a file.
Example 3:
Input: input = "a"
Output: 0
Explanation: We do not have any files, just a single directory named "a".
Constraints:
1 <= input.length <= 10^4inputmay contain lowercase or uppercase English letters, a new line character'\n', a tab character'\t', a dot'.', a space' ', and digits.- All file and directory names have positive length.
题目大意
假设有一个同时存储文件和目录的文件系统。下图展示了文件系统的一个示例:

这里将 dir 作为根目录中的唯一目录。dir 包含两个子目录 subdir1 和 subdir2 。subdir1 包含文件 file1.ext 和子目录 subsubdir1;subdir2 包含子目录 subsubdir2,该子目录下包含文件 file2.ext 。
在文本格式中,如下所示(⟶ 表示制表符):
dir
⟶ subdir1
⟶ ⟶ file1.ext
⟶ ⟶ subsubdir1
⟶ subdir2
⟶ ⟶ subsubdir2
⟶ ⟶ ⟶ file2.ext
如果是代码表示,上面的文件系统可以写为 "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext" 。'\n' 和 '\t' 分别是换行符和制表符。
文件系统中的每个文件和文件夹都有一个唯一的 绝对路径 ,即必须打开才能到达文件/目录所在位置的目录顺序,所有路径用 '/' 连接。上面例子中,指向 file2.ext 的 绝对路径 是 "dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" 。每个目录名由字母、数字和/或空格组成,每个文件名遵循 name.extension 的格式,其中 name 和 extension由字母、数字和/或空格组成。
给定一个以上述格式表示文件系统的字符串 input ,返回文件系统中 指向 文件 的 最长绝对路径 的长度 。 如果系统中没有文件,返回 0。
示例 1:

输入: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tfile.ext"
输出: 20
解释: 只有一个文件,绝对路径为 "dir/subdir2/file.ext" ,路径长度 20
示例 2:

输入: input = "dir\n\tsubdir1\n\t\tfile1.ext\n\t\tsubsubdir1\n\tsubdir2\n\t\tsubsubdir2\n\t\t\tfile2.ext"
输出: 32
解释: 存在两个文件:
"dir/subdir1/file1.ext" ,路径长度 21
"dir/subdir2/subsubdir2/file2.ext" ,路径长度 32
返回 32 ,因为这是最长的路径
示例 3:
输入: input = "a"
输出: 0
解释: 不存在任何文件
示例 4:
输入: input = "file1.txt\nfile2.txt\nlongfile.txt"
输出: 12
解释: 根目录下有 3 个文件。
因为根目录中任何东西的绝对路径只是名称本身,所以答案是 "longfile.txt" ,路径长度为 12
提示:
1 <= input.length <= 10^4input可能包含小写或大写的英文字母,一个换行符'\n',一个制表符'\t',一个点'.',一个空格' ',和数字。
解题思路
解析路径:
将输入字符串通过\n拆分成路径片段,存储到数组arr中。缓存路径长度:
用cache来存储每一层的当前路径长度,初始值为cache.set(0, 0),表示根层路径长度为 0。遍历路径片段:
- 去除
\t得到实际文件名或目录名name,计算其层级depth = str.length - name.length。 - 判断是否为文件 (
name.includes('.')):- 如果是文件,计算完整路径长度并更新
res。
- 如果是文件,计算完整路径长度并更新
- 如果是目录,将其长度缓存
cache.set(depth + 1, cache.get(depth) + name.length + 1)(+1 是因为需要加上/分隔符)。
- 去除
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是字符串的长度,每个字符只处理一次。 - 空间复杂度:
O(d),其中d是目录深度,需要存储每层路径长度。
代码
/**
* @param {string} input
* @return {number}
*/
var lengthLongestPath = function (input) {
const paths = input.split('\n');
let maxLen = 0;
const cache = new Map();
cache.set(0, 0);
for (let path of paths) {
const name = path.replace(/\t/g, '');
const depth = path.length - name.length;
if (name.includes('.')) {
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, cache.get(depth) + name.length);
} else {
cache.set(depth + 1, cache.get(depth) + name.length + 1);
}
}
return maxLen;
};
