375. 猜数字大小 II
375. 猜数字大小 II
题目
We are playing the Guessing Game. The game will work as follows:
- I pick a number between
1andn. - You guess a number.
- If you guess the right number, you win the game.
- If you guess the wrong number, then I will tell you whether the number I picked is higher or lower , and you will continue guessing.
- Every time you guess a wrong number
x, you will payxdollars. If you run out of money, you lose the game.
Given a particular n, return the minimum amount of money you need to guarantee a win regardless of what number I pick.
Example 1:
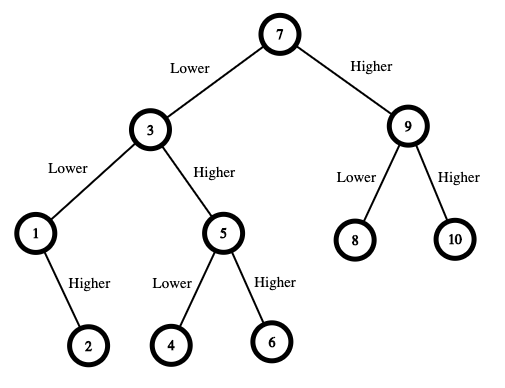
Input: n = 10
Output: 16
Explanation: The winning strategy is as follows:
The range is [1,10]. Guess 7.
If this is my number, your total is $0. Otherwise, you pay $7.
If my number is higher, the range is [8,10]. Guess 9.
If this is my number, your total is $7. Otherwise, you pay $9.
If my number is higher, it must be 10. Guess 10. Your total is $7 + $9 = $16.
If my number is lower, it must be 8. Guess 8. Your total is $7 + $9 = $16.
If my number is lower, the range is [1,6]. Guess 3.
If this is my number, your total is $7. Otherwise, you pay $3.
If my number is higher, the range is [4,6]. Guess 5.
If this is my number, your total is $7 + $3 = $10. Otherwise, you pay $5.
If my number is higher, it must be 6. Guess 6. Your total is $7 + $3 + $5 = $15.
If my number is lower, it must be 4. Guess 4. Your total is $7 + $3 + $5 = $15.
If my number is lower, the range is [1,2]. Guess 1.
If this is my number, your total is $7 + $3 = $10. Otherwise, you pay $1.
If my number is higher, it must be 2. Guess 2. Your total is $7 + $3 + $1 = $11.
The worst case in all these scenarios is that you pay $16. Hence, you only need $16 to guarantee a win.
Example 2:
Input: n = 1
Output: 0
Explanation: There is only one possible number, so you can guess 1 and not have to pay anything.
Example 3:
Input: n = 2
Output: 1
Explanation: There are two possible numbers, 1 and 2.
Guess 1.
If this is my number, your total is $0. Otherwise, you pay $1.
If my number is higher, it must be 2. Guess 2. Your total is $1.
The worst case is that you pay $1.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200
题目大意
我们正在玩一个猜数游戏,游戏规则如下:
- 我从
1到n之间选择一个数字。 - 你来猜我选了哪个数字。
- 如果你猜到正确的数字,就会 赢得游戏 。
- 如果你猜错了,那么我会告诉你,我选的数字比你的 更大或者更小 ,并且你需要继续猜数。
- 每当你猜了数字
x并且猜错了的时候,你需要支付金额为x的现金。如果你花光了钱,就会 输掉游戏 。
给你一个特定的数字 n ,返回能够 确保你获胜 的最小现金数,不管我选择那个数字 。
示例 1:

输入: n = 10
输出: 16
解释: 制胜策略如下:
数字范围是 [1,10] 。你先猜测数字为 7 。
如果这是我选中的数字,你的总费用为 $0 。否则,你需要支付 $7 。
如果我的数字更大,则下一步需要猜测的数字范围是 [8,10] 。你可以猜测数字为 9 。
如果这是我选中的数字,你的总费用为 $7 。否则,你需要支付 $9 。
如果我的数字更大,那么这个数字一定是 10 。你猜测数字为 10 并赢得游戏,总费用为 $7 + $9 = $16 。
如果我的数字更小,那么这个数字一定是 8 。你猜测数字为 8 并赢得游戏,总费用为 $7 + $9 = $16 。
如果我的数字更小,则下一步需要猜测的数字范围是 [1,6] 。你可以猜测数字为 3 。
如果这是我选中的数字,你的总费用为 $7 。否则,你需要支付 $3 。
如果我的数字更大,则下一步需要猜测的数字范围是 [4,6] 。你可以猜测数字为 5 。
如果这是我选中的数字,你的总费用为 $7 + $3 = $10 。否则,你需要支付 $5 。
如果我的数字更大,那么这个数字一定是 6 。你猜测数字为 6 并赢得游戏,总费用为 $7 + $3 + $5 = $15 。
如果我的数字更小,那么这个数字一定是 4 。你猜测数字为 4 并赢得游戏,总费用为 $7 + $3 + $5 = $15 。
如果我的数字更小,则下一步需要猜测的数字范围是 [1,2] 。你可以猜测数字为 1 。
如果这是我选中的数字,你的总费用为 $7 + $3 = $10 。否则,你需要支付 $1 。
如果我的数字更大,那么这个数字一定是 2 。你猜测数字为 2 并赢得游戏,总费用为 $7 + $3 + $1 = $11 。
在最糟糕的情况下,你需要支付 $16 。因此,你只需要 $16 就可以确保自己赢得游戏。
示例 2:
输入: n = 1
输出: 0
解释: 只有一个可能的数字,所以你可以直接猜 1 并赢得游戏,无需支付任何费用。
示例 3:
输入: n = 2
输出: 1
解释: 有两个可能的数字 1 和 2 。
你可以先猜 1 。
如果这是我选中的数字,你的总费用为 $0 。否则,你需要支付 $1 。
如果我的数字更大,那么这个数字一定是 2 。你猜测数字为 2 并赢得游戏,总费用为 $1 。
最糟糕的情况下,你需要支付 $1 。
提示:
1 <= n <= 200
解题思路
这个问题可以用 动态规划(Dynamic Programming, DP) 来解决。我们需要计算在区间 [i, j] 内猜数字的最小成本,然后逐步扩展到整个区间 [1, n]。
定义状态
- 设
dp[i][j]表示在区间[i, j]内猜数字的最小成本。
- 设
状态转移方程
假设第一次猜的数字是
x并且猜错,则需要支付金额x;- 当
x大于所选数字时,为了确保胜利还需要支付的金额是dp[1, x - 1]; - 当
x小于所选数字时,为了确保胜利还需要支付的金额是dp[x + 1, n]。
- 当
为了在任何情况下都能确保胜利,应考虑最坏情况,计算
dp[1, n]时应取上述两者的最大值:dp[1, n] = x + max(dp[1, x − 1], dp[x + 1, n])。为了将确保胜利的金额最小化,需要遍历从
1到n的所有可能的x,使得dp[1, n]的值最小:dp[1, n] = min(x + max(dp[1, x − 1], dp[x + 1, n])) (1 ≤ x ≤ n)
初始化
- 当
i >= j时,区间无效或只有一个数字,成本为0,即dp[i][j] = 0。
- 当
边界问题
- 在根据状态转移方程计算时需要注意下标的边界问题;
- 当
j = n时,如果x = j则x + 1 > n,此时dp[x][j]会出现下标越界。 - 为了避免出现下标越界,计算
dp[i][j]的方法是:- 首先令
dp[i][j] = j + dp[i][j - 1]; - 然后遍历
i ≤ x < j的每个 x,更新dp[i][j]的值。
- 首先令
最终结果
- 答案是
dp[1][n],即在区间[1, n]内猜数字的最小成本。
- 答案是
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n^3),三重循环。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n^2),DP 表的大小。
代码
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var getMoneyAmount = function (n) {
// 初始化 DP 表
const dp = new Array(n + 1).fill(0).map(() => new Array(n + 1).fill(0));
// 遍历区间起点
for (let i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
// 遍历区间终点
for (let j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
dp[i][j] = j + dp[i][j - 1];
// 遍历所有可能的猜测点 x
for (let x = i; x < j; x++) {
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i][j], x + Math.max(dp[i][x - 1], dp[x + 1][j]));
}
}
}
return dp[1][n];
};
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 294 | 翻转游戏 II 🔒 | 记忆化搜索 数学 动态规划 2+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 374 | 猜数字大小 | [✓] | 二分查找 交互 | 🟢 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 464 | 我能赢吗 | [✓] | 位运算 记忆化搜索 数学 3+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 658 | 找到 K 个最接近的元素 | [✓] | 数组 双指针 二分查找 3+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
