404. 左叶子之和
404. 左叶子之和
🟢 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
Given the root of a binary tree, return the sum of all left leaves.
A leaf is a node with no children. A left leaf is a leaf that is the left child of another node.
Example 1:
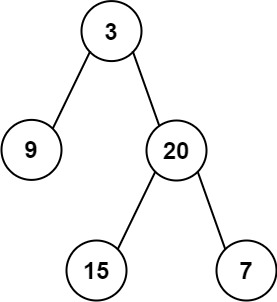
Input: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
Output: 24
Explanation: There are two left leaves in the binary tree, with values 9 and 15 respectively.
Example 2:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
题目大意
给定二叉树的根节点 root ,返回所有左叶子之和。
示例 1:

输入: root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出: 24
解释: 在这个二叉树中,有两个左叶子,分别是 9 和 15,所以返回 24
示例 2:
输入: root = [1]
输出: 0
提示:
- 节点数在
[1, 1000]范围内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
解题思路
思路一:递归
- 当前节点:
- 判断其左子节点是否是 左叶子节点。
- 如果是,则将左子节点的值加入到结果中。
- 判断其左子节点是否是 左叶子节点。
- 递归向下:
- 分别对当前节点的左子树和右子树进行递归操作。
- 返回结果:将所有左叶子节点的值累加并返回。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),每个节点遍历一次,n是树中的节点总数。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n),取决于递归调用栈的深度,最坏情况下是O(n)(链状树)。
思路二:迭代(BFS)
- 使用队列进行 层序遍历。
- 遍历过程中:
- 如果当前节点的左子节点是 左叶子,将其值加入结果中。
- 将左右子节点继续加入队列,继续遍历。
- 返回累加的结果。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),每个节点遍历一次,n是树中的节点总数。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n),取决于队列的最大长度,最坏情况下是O(n)。
代码
递归
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function (root) {
if (!root) return 0;
let sum = 0;
// 判断左子节点是否是左叶子节点
if (root.left && !root.left.left && !root.left.right) {
sum += root.left.val;
}
// 递归左右子树
sum += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
sum += sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
return sum;
};
迭代(BFS)
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var sumOfLeftLeaves = function (root) {
if (!root) return 0;
let sum = 0;
let queue = [root];
while (queue.length > 0) {
let node = queue.shift();
// 检查左子节点是否是左叶子
if (node.left && !node.left.left && !node.left.right) {
sum += node.left.val;
}
// 继续遍历左右子树
if (node.left) queue.push(node.left);
if (node.right) queue.push(node.right);
}
return sum;
};
