235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
235. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
🟠 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 二叉搜索树 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
Given a binary search tree (BST), find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) node of two given nodes in the BST.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: "The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself )."
Example 1:
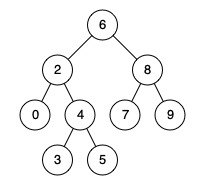
Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 8
Output: 6
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 8 is 6.
Example 2:

Input: root = [6,2,8,0,4,7,9,null,null,3,5], p = 2, q = 4
Output: 2
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 2 and 4 is 2, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
Example 3:
Input: root = [2,1], p = 2, q = 1
Output: 2
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 10^5]. -10^9 <= Node.val <= 10^9- All
Node.valare unique. p != qpandqwill exist in the BST.
题目大意
给定一个二叉搜索树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
维基百科中最近公共祖先的定义为:“对于有根树 T 的两个结点 p、q,最近公共祖先表示为一个结点 x,满足 x 是 p、q 的祖先且 x 的深度尽可能大(一个节点也可以是它自己的祖先)。”
解题思路
思路一:递归比数值
由于 BST 的性质,可以通过比较节点的值来确定最近的公共祖先。
- 如果节点的值小于
p和q的值,说明p和q都在节点的右子树中,递归搜索右子树。 - 如果节点的值大于
p和q的值,说明p和q都在节点的左子树中,递归搜索左子树。 - 如果节点的值在
p和q的值之间,说明当前节点即为最近的公共祖先。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(h),其中h是树的高度,在二叉搜索树中,查找最近公共祖先的时间复杂度为O(h)。- 对于平衡的二叉搜索树,
h = log n,其中n是树中节点的总数,因此时间复杂度在平衡情况下为O(log n)。 - 在最坏情况下(例如树呈线性结构),时间复杂度为
O(n)。
- 对于平衡的二叉搜索树,
- 空间复杂度:
O(h),其中h是树的高度,空间复杂度主要由递归调用栈的深度决定。- 对于平衡的二叉搜索树,空间复杂度为
O(log n),其中n是树中节点的总数。 - 在最坏情况下(例如,树是完全不平衡的),递归的深度可以达到
O(n)。
- 对于平衡的二叉搜索树,空间复杂度为
思路二:递归查找
和 第 236 题 一样,使用递归查找。
从根节点开始,递归地向左子树和右子树搜索。递归的终止条件有几种情况:
- 如果当前节点为
null,表示遍历到空节点,直接返回null。 - 如果当前节点等于
p或q,表示找到了其中一个节点,直接返回当前节点。
递归步骤如下:
- 递归地在左子树中寻找
p和q的最低共同祖先,结果存储在变量left中。 - 递归地在右子树中寻找
p和q的最低共同祖先,结果存储在变量right中。
然后,根据 left 和 right 的情况,可以得出以下结论:
- 如果
left和right都不为null,说明p和q分别位于当前节点的左右子树,因此当前节点就是它们的最低共同祖先,直接返回当前节点。 - 如果只有
left不为null,说明p和q都在左子树,最低共同祖先在左子树中,返回left。 - 如果只有
right不为null,说明p和q都在右子树,最低共同祖先在右子树中,返回right。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是树中节点的总数,因为在最坏的情况下,需要检查每个节点来找到最近公共祖先。 - 空间复杂度:
O(h),其中h是树的高度,空间复杂度主要由递归调用栈的深度决定。- 在平衡树中,递归深度为
O(h),其中h是树的高度。 - 在最坏情况下(例如,树是完全不平衡的),递归的深度可以达到
O(n),其中n是树中节点的总数。
- 在平衡树中,递归深度为
代码
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {
if (!root) return null;
if (root.val < p.val && root.val < q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
} else if (root.val > p.val && root.val > q.val) {
return lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
}
return root;
};
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @param {TreeNode} p
* @param {TreeNode} q
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var lowestCommonAncestor = function (root, p, q) {
if (!root || p == root || q == root) return root;
let left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
let right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
if (left && right) return root;
return left ? left : right;
};
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 236 | 二叉树的最近公共祖先 | [✓] | 树 深度优先搜索 二叉树 | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
| 1257 | 最小公共区域 🔒 | 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 3+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 1644 | 二叉树的最近公共祖先 II 🔒 | 树 深度优先搜索 二叉树 | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 1650 | 二叉树的最近公共祖先 III 🔒 | 树 哈希表 双指针 1+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 1676 | 二叉树的最近公共祖先 IV 🔒 | 树 深度优先搜索 哈希表 1+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
