1372. 二叉树中的最长交错路径
1372. 二叉树中的最长交错路径
🟠 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 动态规划 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
You are given the root of a binary tree.
A ZigZag path for a binary tree is defined as follow:
- Choose any node in the binary tree and a direction (right or left).
- If the current direction is right, move to the right child of the current node; otherwise, move to the left child.
- Change the direction from right to left or from left to right.
- Repeat the second and third steps until you can't move in the tree.
Zigzag length is defined as the number of nodes visited - 1. (A single node has a length of 0).
Return the longestZigZag path contained in that tree.
Example 1:
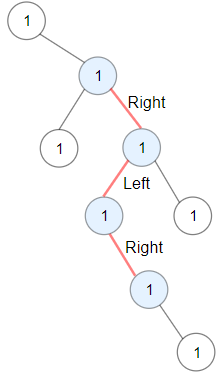
Input: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1]
Output: 3
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (right -> left -> right).
Example 2:
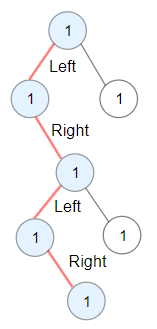
Input: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Longest ZigZag path in blue nodes (left -> right -> left -> right).
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: 0
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 5 * 104]. 1 <= Node.val <= 100
题目大意
给你一棵以 root 为根的二叉树,二叉树中的交错路径定义如下:
- 选择二叉树中 任意 节点和一个方向(左或者右)。
- 如果前进方向为右,那么移动到当前节点的的右子节点,否则移动到它的左子节点。
- 改变前进方向:左变右或者右变左。
- 重复第二步和第三步,直到你在树中无法继续移动。
交错路径的长度定义为:访问过的节点数目 - 1 (单个节点的路径长度为 0 )。
请你返回给定树中最长 交错路径 的长度。
示例 1:

输入: root = [1,null,1,1,1,null,null,1,1,null,1,null,null,null,1,null,1]
输出: 3
解释: 蓝色节点为树中最长交错路径(右 -> 左 -> 右)。
示例 2:

输入: root = [1,1,1,null,1,null,null,1,1,null,1]
输出: 4
解释: 蓝色节点为树中最长交错路径(左 -> 右 -> 左 -> 右)。
示例 3:
输入: root = [1]
输出: 0
提示:
- 每棵树最多有
50000个节点。 - 每个节点的值在
[1, 100]之间。
解题思路
使用深度优先搜索(DFS)遍历整棵树,在每个节点上记录当前路径是向左延伸还是向右延伸,以及当前路径的长度。
在递归过程中:
如果节点为空,则直接返回;
在每个节点上,记录当前路径长度,并尝试更新全局最大值。
如果当前路径是向左延伸:
- 对左子节点重新开始,路径长度重置为 1;
- 对右子节点继续延长,路径长度加 1。
如果当前路径是向右延伸:
- 对右子节点重新开始,路径长度重置为 1;
- 对左子节点继续延长,路径长度加 1。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是节点数,每个节点访问一次。 - 空间复杂度:
O(h),其中h是树的高度,递归调用栈的深度为树的高度。
代码
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var longestZigZag = function (root) {
if (!root) return 0; // 空树直接返回
let maxZigZag = 0; // 记录最长交错路径
// 定义递归函数
const traverse = (node, isLeft, length) => {
if (!node) return; // 遇到空节点直接返回
maxZigZag = Math.max(maxZigZag, length); // 更新最长路径
if (isLeft) {
// 当前路径是向左延伸
traverse(node.left, true, 1); // 左子节点重新开始
traverse(node.right, false, length + 1); // 右子节点延长路径
} else {
// 当前路径是向右延伸
traverse(node.left, true, length + 1); // 左子节点延长路径
traverse(node.right, false, 1); // 右子节点重新开始
}
};
// 分别从根节点的左右子树开始
traverse(root.left, true, 1); // 向左延伸
traverse(root.right, false, 1); // 向右延伸
return maxZigZag;
};
