897. 递增顺序搜索树
897. 递增顺序搜索树
🟢 🔖 栈 树 深度优先搜索 二叉搜索树 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
Given the root of a binary search tree, rearrange the tree in in-order so that the leftmost node in the tree is now the root of the tree, and every node has no left child and only one right child.
Example 1:
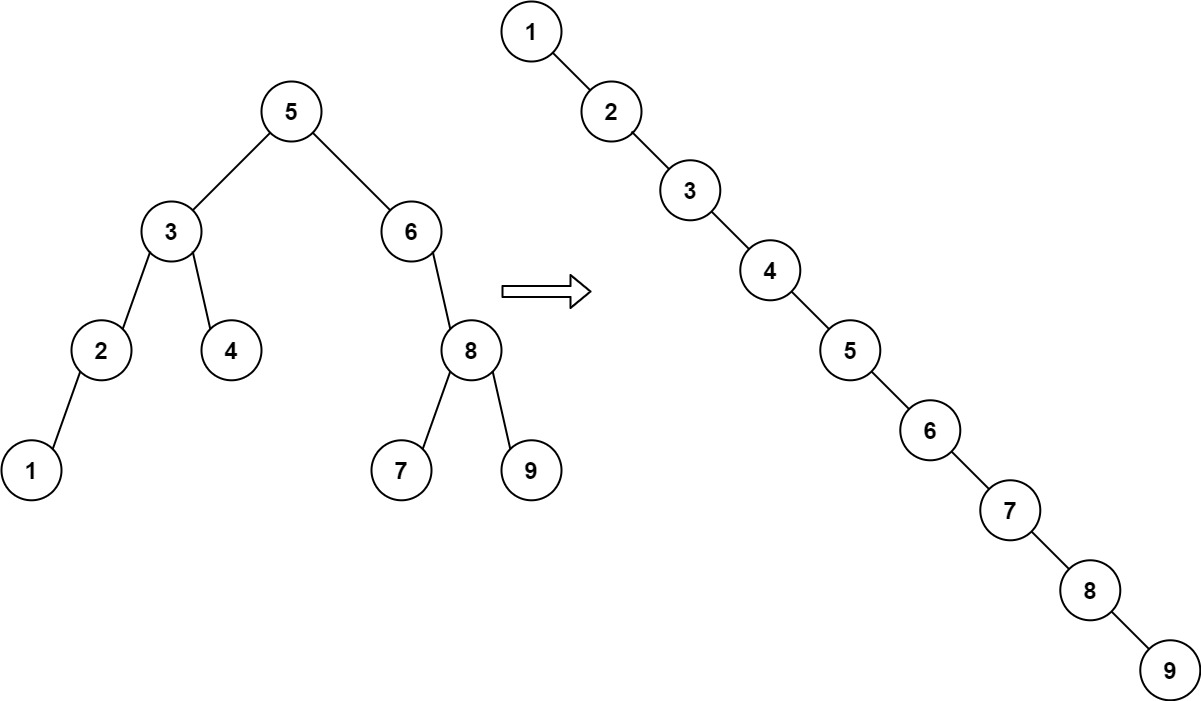
Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9]
Output: [1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]
Example 2:
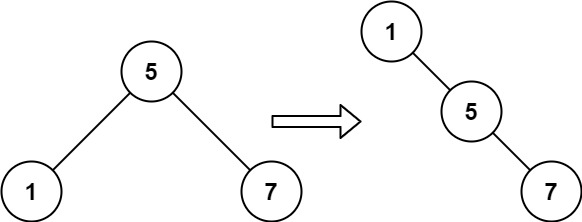
Input: root = [5,1,7]
Output: [1,null,5,null,7]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the given tree will be in the range
[1, 100]. 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
题目大意
给你一棵二叉搜索树的 root ,请你 按中序遍历 将其重新排列为一棵递增顺序搜索树,使树中最左边的节点成为树的根节点,并且每个节点没有左子节点,只有一个右子节点。
示例 1:

输入: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,8,1,null,null,null,7,9]
输出:[1,null,2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6,null,7,null,8,null,9]
示例 2:

输入: root = [5,1,7]
输出:[1,null,5,null,7]
提示:
- 树中节点数的取值范围是
[1, 100] 0 <= Node.val <= 1000
解题思路
二叉搜索树的中序遍历得到的结果是一个递增序列。
使用一个 哑节点(dummy node)作为新树的起点。
用一个指针
curr记录当前新树的构造位置。中序遍历的每一步:
- 将当前节点的左子节点清空(因为新树没有左子节点)。
- 将当前节点连接到新树的右子节点。
- 更新
curr为当前节点。
返回结果:哑节点的右子节点即为新树的根节点。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是树中节点的数量,中序遍历访问每个节点一次。 - 空间复杂度:
O(h),其中h是树的高度,递归栈的深度取决于树的高度,最坏情况下为O(h)。
代码
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var increasingBST = function (root) {
let dummy = new TreeNode(-1); // 创建一个哑节点作为新树的起点
let curr = dummy;
const inorder = (node) => {
if (!node) return;
inorder(node.left); // 递归左子树
node.left = null; // 清理左子节点
curr.right = node; // 将当前节点接到新树的右子树
curr = node; // 更新当前指针
inorder(node.right); // 递归右子树
};
inorder(root);
return dummy.right; // 返回哑节点的右子节点,即新树的根
};
