773. 滑动谜题
773. 滑动谜题
🔴 🔖 广度优先搜索 数组 矩阵 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
On an 2 x 3 board, there are five tiles labeled from 1 to 5, and an empty square represented by 0. A move consists of choosing 0 and a 4-directionally adjacent number and swapping it.
The state of the board is solved if and only if the board is [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]].
Given the puzzle board board, return the least number of moves required so that the state of the board is solved. If it is impossible for the state of the board to be solved, return -1.
Example 1:
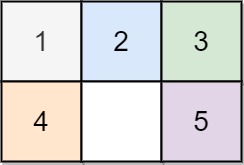
Input: board = [[1,2,3],[4,0,5]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Swap the 0 and the 5 in one move.
Example 2:
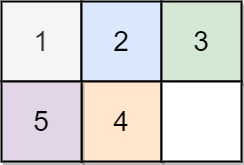
Input: board = [[1,2,3],[5,4,0]]
Output: -1
Explanation: No number of moves will make the board solved.
Example 3:
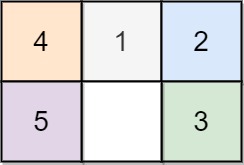
Input: board = [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]]
Output: 5
Explanation: 5 is the smallest number of moves that solves the board.
An example path:
After move 0: [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]]
After move 1: [[4,1,2],[0,5,3]]
After move 2: [[0,1,2],[4,5,3]]
After move 3: [[1,0,2],[4,5,3]]
After move 4: [[1,2,0],[4,5,3]]
After move 5: [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]]
Constraints:
board.length == 2board[i].length == 30 <= board[i][j] <= 5- Each value
board[i][j]is unique.
题目大意
在一个 2 x 3 的板上(board)有 5 块砖瓦,用数字 1~5 来表示, 以及一块空缺用 0 来表示。一次 移动 定义为选择 0 与一个相邻的数字(上下左右)进行交换.
最终当板 board 的结果是 [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]] 谜板被解开。
给出一个谜板的初始状态 board ,返回最少可以通过多少次移动解开谜板,如果不能解开谜板,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:

输入: board = [[1,2,3],[4,0,5]]
输出: 1
解释: 交换 0 和 5 ,1 步完成
示例 2:

输入: board = [[1,2,3],[5,4,0]]
输出: -1
解释: 没有办法完成谜板
示例 3:

输入: board = [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]]
输出: 5
解释:
最少完成谜板的最少移动次数是 5 ,
一种移动路径:
尚未移动: [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]]
移动 1 次: [[4,1,2],[0,5,3]]
移动 2 次: [[0,1,2],[4,5,3]]
移动 3 次: [[1,0,2],[4,5,3]]
移动 4 次: [[1,2,0],[4,5,3]]
移动 5 次: [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]]
提示:
board.length == 2board[i].length == 30 <= board[i][j] <= 5board[i][j]中每个值都 不同
解题思路
这是一个典型的 状态空间搜索问题,可以通过 广度优先搜索(BFS) 寻找从初始状态到目标状态的最短路径。
状态表示:
- 将
2 * 3的拼图转换为字符串表示(如"123450"),以便表示状态。 - 空格
0的位置决定了可以进行的移动。
- 将
状态转移:
- 定义每个位置(索引)的合法移动方向。例如:
- 索引
0的合法移动位置为[1,3](右、下)。 - 索引
4的合法移动位置为[1,3,5](上、左、右)。
- 索引
- 预定义一个方向数组表示索引间的相邻关系。
- 定义每个位置(索引)的合法移动方向。例如:
BFS 搜索:
- 将初始状态加入队列,使用 BFS 搜索所有可能的状态。
- 每次弹出队列中的状态,将空格
0和其相邻位置的数字交换,生成新的状态。 - 如果新状态是目标状态,则返回当前步数。
- 使用集合记录已访问状态,避免重复计算。
- 若队列为空且未找到目标状态,返回
-1。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
O((m * n)!),最多需要遍历所有状态,状态总数为(m * n)!(这里m * n = 6),每个状态需要O(m * n)的字符串操作。空间复杂度:
O((m * n)!),队列与集合的空间复杂度由状态数量决定。
代码
/**
* @param {number[][]} board
* @return {number}
*/
var slidingPuzzle = function (board) {
const target = '123450'; // 目标状态
const start = board.flat().join(''); // 初始状态
// 每个索引的合法移动位置
const neighbors = [
[1, 3], // 0
[0, 2, 4], // 1
[1, 5], // 2
[0, 4], // 3
[1, 3, 5], // 4
[2, 4] // 5
];
// BFS 初始化
const queue = [[start, 0]]; // [状态, 步数]
const visited = new Set();
visited.add(start);
while (queue.length) {
const [state, steps] = queue.shift();
if (state === target) return steps; // 找到目标状态
const zeroIndex = state.indexOf('0'); // 找到空格位置
for (let neighbor of neighbors[zeroIndex]) {
// 交换空格与邻居位置
const newState = swap(state, zeroIndex, neighbor);
if (!visited.has(newState)) {
visited.add(newState);
queue.push([newState, steps + 1]);
}
}
}
return -1; // 无法到达目标状态
};
// 辅助函数:交换字符串中两个索引位置的字符
function swap(str, i, j) {
const arr = str.split('');
[arr[i], arr[j]] = [arr[j], arr[i]];
return arr.join('');
}
