1976. 到达目的地的方案数
1976. 到达目的地的方案数
🟠 🔖 图 拓扑排序 动态规划 最短路 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
You are in a city that consists of n intersections numbered from 0 to n - 1 with bi-directional roads between some intersections. The inputs are generated such that you can reach any intersection from any other intersection and that there is at most one road between any two intersections.
You are given an integer n and a 2D integer array roads where roads[i] = [ui, vi, timei] means that there is a road between intersections ui and vi that takes timei minutes to travel. You want to know in how many ways you can travel from intersection 0 to intersection n - 1 in the shortest amount of time.
Return the number of ways you can arrive at your destination in the shortest amount of time. Since the answer may be large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
Example 1:
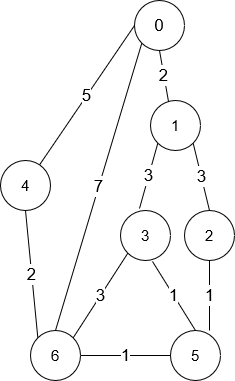
Input: n = 7, roads = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The shortest amount of time it takes to go from intersection 0 to intersection 6 is 7 minutes.
The four ways to get there in 7 minutes are:
- 0 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 4 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 2 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 3 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
Example 2:
Input: n = 2, roads = [[1,0,10]]
Output: 1
Explanation: There is only one way to go from intersection 0 to intersection 1, and it takes 10 minutes.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 200n - 1 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= timei <= 10^9ui != vi- There is at most one road connecting any two intersections.
- You can reach any intersection from any other intersection.
题目大意
你在一个城市里,城市由 n 个路口组成,路口编号为 0 到 n - 1 ,某些路口之间有 双向 道路。输入保证你可以从任意路口出发到达其他任意路口,且任意两个路口之间最多有一条路。
给你一个整数 n 和二维整数数组 roads ,其中 roads[i] = [ui, vi, timei] 表示在路口 ui 和 vi 之间有一条需要花费 timei 时间才能通过的道路。你想知道花费 最少时间 从路口 0 出发到达路口 n - 1 的方案数。
请返回花费 最少时间 到达目的地的 路径数目 。由于答案可能很大,将结果对 10^9 + 7 取余 后返回。
示例 1:

输入: n = 7, roads = [[0,6,7],[0,1,2],[1,2,3],[1,3,3],[6,3,3],[3,5,1],[6,5,1],[2,5,1],[0,4,5],[4,6,2]]
输出: 4
解释: 从路口 0 出发到路口 6 花费的最少时间是 7 分钟。
四条花费 7 分钟的路径分别为:
- 0 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 4 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 2 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
- 0 ➝ 1 ➝ 3 ➝ 5 ➝ 6
示例 2:
输入: n = 2, roads = [[1,0,10]]
输出: 1
解释: 只有一条从路口 0 到路口 1 的路,花费 10 分钟。
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n - 1 <= roads.length <= n * (n - 1) / 2roads[i].length == 30 <= ui, vi <= n - 11 <= timei <= 10^9ui != vi- 任意两个路口之间至多有一条路。
- 从任意路口出发,你能够到达其他任意路口。
解题思路
使用 Dijkstra 算法寻找最短路径
- 为什么用 Dijkstra:
- 由于图中边的权重非负,Dijkstra 算法能够高效地找到从起点到每个节点的最短路径。
- 同时,Dijkstra 算法的遍历顺序可以自然地记录到达每个节点的最短路径数量。
- 如何表示图:
- 用邻接表
graph表示图,其中graph[u]包含所有与u相邻的节点及到达时间[v, time]。
- 用邻接表
- 为什么用 Dijkstra:
初始化
dist和ways数组dist[i]:表示从起点0到节点i的最短距离,初始值为Infinity。ways[i]:表示从起点0到节点i的最短路径数量,初始值为0。- 设置
dist[0] = 0和ways[0] = 1。
使用最小堆(Min Heap)来优化遍历顺序
- 为什么用最小堆:
- 每次从堆中弹出当前距离最短的节点,能够避免遍历所有节点,提升效率。
- 堆中元素为
[time, node],表示当前节点及到达所需的总时间。
- 为什么用最小堆:
遍历图并更新最短路径
- 对每个相邻节点:
- 计算从当前节点到相邻节点的总时间
newTime。 - 如果
newTime < dist[neighbor]:- 说明找到了一条更短的路径,更新
dist[neighbor]为newTime。 - 将
ways[neighbor]更新为ways[node](即当前节点路径数量)。 - 将
neighbor节点及其距离加入堆中。
- 说明找到了一条更短的路径,更新
- 如果
newTime === dist[neighbor]:- 说明找到了一条与最短路径等长的路径,将
ways[neighbor]累加上ways[node]。
- 说明找到了一条与最短路径等长的路径,将
- 计算从当前节点到相邻节点的总时间
- 对每个相邻节点:
输出结果
- 返回
ways[n - 1],即到达终点节点n - 1的最短路径数量,并对10^9 + 7取模。
- 返回
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
O((e + n) * log n),其中,e为roads的长度,也就是图中有多少条边。- 遍历
e条边的时间复杂度为O(e)。 - 使用最小堆,每次
insert和pop的时间复杂度为O(log n),最多进行n次操作。
- 遍历
空间复杂度:
O(e + n)- 需要存储邻接表
graph、dist数组、ways数组、以及最小堆heap。 - 总空间需求与
e和n呈线性关系。
- 需要存储邻接表
代码
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} roads
* @return {number}
*/
var countPaths = function (n, roads) {
const MOD = 1e9 + 7;
// 构建图
let graph = new Array(n).fill().map(() => []);
for (let [u, v, time] of roads) {
graph[u].push([v, time]);
graph[v].push([u, time]);
}
// 初始化
let dist = new Array(n).fill(Infinity);
let ways = new Array(n).fill(0);
dist[0] = 0;
ways[0] = 1;
// 使用最小堆(优先队列)
let heap = new MinHeap([[0, 0]], (a, b) => a[0] < b[0]);
while (heap.size() > 0) {
const [time, node] = heap.pop();
// 跳过已更新的更短路径
if (time > dist[node]) continue;
for (let [neighbor, t] of graph[node]) {
const newTime = time + t;
if (newTime < dist[neighbor]) {
// 找到更短路径,更新最短距离和路径数
dist[neighbor] = newTime;
ways[neighbor] = ways[node];
heap.insert([newTime, neighbor]);
} else if (newTime === dist[neighbor]) {
// 如果路径长度相同,累加路径数
ways[neighbor] = (ways[neighbor] + ways[node]) % MOD;
}
}
}
return ways[n - 1];
};
class MinHeap {
constructor(arr = [], priority = (a, b) => a < b) {
this.heap = arr;
this.priority = priority;
for (let i = Math.floor(this.heap.length / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
this.heapifyDown(i);
}
}
insert(num) {
this.heap.push(num);
this.heapifyUp(this.heap.length - 1);
}
pop() {
if (this.heap.length === 0) return null;
const top = this.heap[0];
const last = this.heap.pop();
if (this.heap.length > 0) {
this.heap[0] = last;
this.heapifyDown(0);
}
return top;
}
isEmpty() {
return this.heap.length == 0;
}
size() {
return this.heap.length;
}
heapifyDown(i) {
const n = this.heap.length;
const left = 2 * i + 1;
const right = 2 * i + 2;
let smallest = i;
if (left < n && this.priority(this.heap[left], this.heap[smallest])) {
smallest = left;
}
if (right < n && this.priority(this.heap[right], this.heap[smallest])) {
smallest = right;
}
if (smallest !== i) {
[this.heap[i], this.heap[smallest]] = [this.heap[smallest], this.heap[i]];
this.heapifyDown(smallest);
}
}
heapifyUp(i) {
while (i > 0) {
const parent = Math.floor((i - 1) / 2);
if (this.priority(this.heap[i], this.heap[parent])) {
[this.heap[i], this.heap[parent]] = [this.heap[parent], this.heap[i]];
i = parent;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
}
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 797 | 所有可能的路径 | 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 图 1+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 1514 | 概率最大的路径 | 图 数组 最短路 1+ | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 | |
| 2045 | 到达目的地的第二短时间 | 广度优先搜索 图 最短路 | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
