1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口
1926. 迷宫中离入口最近的出口
🟠 🔖 广度优先搜索 数组 矩阵 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
You are given an m x n matrix maze (0-indexed) with empty cells (represented as '.') and walls (represented as '+'). You are also given the entrance of the maze, where entrance = [entrancerow, entrancecol] denotes the row and column of the cell you are initially standing at.
In one step, you can move one cell up , down , left , or right. You cannot step into a cell with a wall, and you cannot step outside the maze. Your goal is to find the nearest exit from the entrance. An exit is defined as an empty cell that is at the border of the maze. The entrance does not count as an exit.
Return _thenumber of steps in the shortest path from the _entrance to the nearest exit, or-1 if no such path exists.
Example 1:
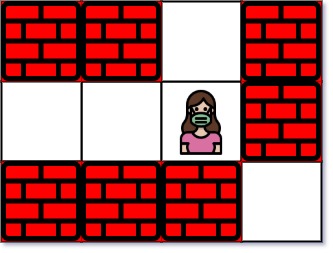
Input: maze = [["+","+",".","+"],[".",".",".","+"],["+","+","+","."]], entrance = [1,2]
Output: 1
Explanation: There are 3 exits in this maze at [1,0], [0,2], and [2,3].
Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,2].
- You can reach [1,0] by moving 2 steps left.
- You can reach [0,2] by moving 1 step up.
It is impossible to reach [2,3] from the entrance.
Thus, the nearest exit is [0,2], which is 1 step away.
Example 2:
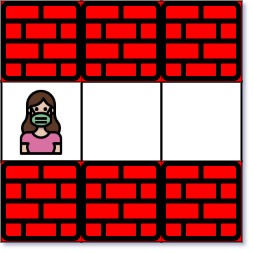
Input: maze = [["+","+","+"],[".",".","."],["+","+","+"]], entrance = [1,0]
Output: 2
Explanation: There is 1 exit in this maze at [1,2].
[1,0] does not count as an exit since it is the entrance cell.
Initially, you are at the entrance cell [1,0].
- You can reach [1,2] by moving 2 steps right.
Thus, the nearest exit is [1,2], which is 2 steps away.
Example 3:

Input: maze = [[".","+"]], entrance = [0,0]
Output: -1
Explanation: There are no exits in this maze.
Constraints:
maze.length == mmaze[i].length == n1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]is either'.'or'+'.entrance.length == 20 <= entrancerow < m0 <= entrancecol < nentrancewill always be an empty cell.
题目大意
给你一个 m x n 的迷宫矩阵 maze (下标从 0 开始 ),矩阵中有空格子(用 '.' 表示)和墙(用 '+' 表示)。同时给你迷宫的入口 entrance ,用 entrance = [entrancerow, entrancecol] 表示你一开始所在格子的行和列。
每一步操作,你可以往 上 ,下 ,左 或者 右 移动一个格子。你不能进入墙所在的格子,你也不能离开迷宫。你的目标是找到离 entrance 最近 的出口。出口 的含义是 maze 边界 上的 空格子 。entrance 格子 不算 出口。
请你返回从 entrance 到最近出口的最短路径的 步数 ,如果不存在这样的路径,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:

输入: maze = [["+","+",".","+"],[".",".",".","+"],["+","+","+","."]], entrance = [1,2]
输出: 1
解释: 总共有 3 个出口,分别位于 (1,0),(0,2) 和 (2,3) 。
一开始,你在入口格子 (1,2) 处。
- 你可以往左移动 2 步到达 (1,0) 。
- 你可以往上移动 1 步到达 (0,2) 。
从入口处没法到达 (2,3) 。
所以,最近的出口是 (0,2) ,距离为 1 步。
示例 2:

输入: maze = [["+","+","+"],[".",".","."],["+","+","+"]], entrance = [1,0]
输出: 2
解释: 迷宫中只有 1 个出口,在 (1,2) 处。
(1,0) 不算出口,因为它是入口格子。
初始时,你在入口与格子 (1,0) 处。
- 你可以往右移动 2 步到达 (1,2) 处。
所以,最近的出口为 (1,2) ,距离为 2 步。
示例 3:

输入: maze = [[".","+"]], entrance = [0,0]
输出: -1
解释: 这个迷宫中没有出口。
提示:
maze.length == mmaze[i].length == n1 <= m, n <= 100maze[i][j]要么是'.',要么是'+'。entrance.length == 20 <= entrancerow < m0 <= entrancecol < nentrance一定是空格子。
解题思路
可以将迷宫抽象为图,网格的每个空格子 '.' 是图的节点,相邻的上下左右方向可以看作边,表示可以移动到下一个节点。
利用 广度优先搜索(BFS) 遍历图,因为 BFS 会优先找到距离入口最近的出口。同时记录已访问过的节点,避免重复遍历。
- 初始化队列
queue,存储当前节点坐标及其到入口的步数[row, col, steps]。 - 将入口坐标加入队列并标记为已访问。
- 开始 BFS:
- 每次从队列中取出一个节点。
- 遍历其上下左右的相邻节点:
- 如果该节点是出口,返回步数。
- 如果该节点是未访问的空格子,则加入队列并标记为已访问。
- 如果所有节点都遍历完,仍无出口,则返回 -1。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(m * n),其中m和n分别是迷宫的行数和列数。使用 BFS 遍历迷宫时,每个节点最多被访问一次,总访问的节点数为O(m * n),每次访问会检查其最多 4 个邻居(上下左右),邻居检查的次数与节点数成比例。 - 空间复杂度:
O(m * n)。- 队列空间:在最坏情况下,队列中可能同时存储所有未访问节点。
- 标记空间:直接在输入的
maze中标记已访问节点,因此不需要额外的访问标记数组。
代码
/**
* @param {character[][]} maze
* @param {number[]} entrance
* @return {number}
*/
var nearestExit = function (maze, entrance) {
const rows = maze.length;
const cols = maze[0].length;
const directions = [
[-1, 0], // 上
[1, 0], // 下
[0, -1], // 左
[0, 1] // 右
];
// 初始化队列和访问标记
const queue = [[entrance[0], entrance[1], 0]]; // [row, col, steps]
maze[entrance[0]][entrance[1]] = '+'; // 标记入口为已访问
while (queue.length > 0) {
const [row, col, steps] = queue.shift();
for (const [dr, dc] of directions) {
const newRow = row + dr;
const newCol = col + dc;
// 检查新位置是否有效且未访问
if (
newRow >= 0 &&
newRow < rows &&
newCol >= 0 &&
newCol < cols &&
maze[newRow][newCol] === '.'
) {
// 检查是否为出口
if (
newRow === 0 ||
newRow === rows - 1 ||
newCol === 0 ||
newCol === cols - 1
) {
return steps + 1;
}
// 标记为已访问并加入队列
maze[newRow][newCol] = '+';
queue.push([newRow, newCol, steps + 1]);
}
}
}
return -1; // 没有找到出口
};
