1886. 判断矩阵经轮转后是否一致
1886. 判断矩阵经轮转后是否一致
题目
Given two n x n binary matrices mat and target, return true if it is possible to makemat equal totarget _by rotating _mat _in90-degree increments , or _false otherwise.
Example 1:
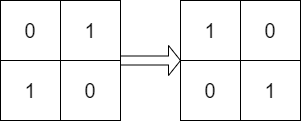
Input: mat = [[0,1],[1,0]], target = [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: true
Explanation: We can rotate mat 90 degrees clockwise to make mat equal target.
Example 2:
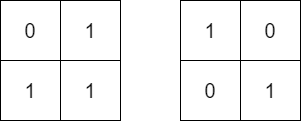
Input: mat = [[0,1],[1,1]], target = [[1,0],[0,1]]
Output: false
Explanation: It is impossible to make mat equal to target by rotating mat.
Example 3:
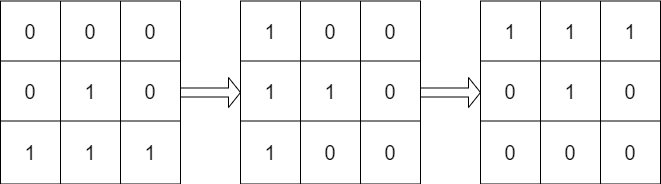
Input: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]], target = [[1,1,1],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
Output: true
Explanation: We can rotate mat 90 degrees clockwise two times to make mat equal target.
Constraints:
n == mat.length == target.lengthn == mat[i].length == target[i].length1 <= n <= 10mat[i][j]andtarget[i][j]are either0or1.
题目大意
给你两个大小为 n x n 的二进制矩阵 mat 和 target 。现以 90 度顺时针轮转 矩阵 mat 中的元素 若干次 ,如果能够使 mat 与 target 一致,返回 true ;否则,返回 false。
示例 1:

输入: mat = [[0,1],[1,0]], target = [[1,0],[0,1]]
输出: true
解释: 顺时针轮转 90 度一次可以使 mat 和 target 一致。
示例 2:

输入: mat = [[0,1],[1,1]], target = [[1,0],[0,1]]
输出: false
解释: 无法通过轮转矩阵中的元素使 equal 与 target 一致。
示例 3:

输入: mat = [[0,0,0],[0,1,0],[1,1,1]], target = [[1,1,1],[0,1,0],[0,0,0]]
输出: true
解释: 顺时针轮转 90 度两次可以使 mat 和 target 一致。
提示:
n == mat.length == target.lengthn == mat[i].length == target[i].length1 <= n <= 10mat[i][j]和target[i][j]不是0就是1
解题思路
要判断矩阵 mat 是否能够通过旋转来变成目标矩阵 target。
我们并不需要真的旋转矩阵然后再逐行逐列地对比是否全等,而只需要直接计算 mat[i][j] 与四种(0 度、90 度、180 度、270 度)可能旋转后对应的坐标是否匹配来判断。
初始化变量
用四个变量分别表示四种旋转后的匹配情况:
normal: 是否原矩阵与目标矩阵相同,即未旋转(0 度)。rightOnce: 是否矩阵经过 90 度旋转后与目标矩阵相同。rightTwice: 是否矩阵经过 180 度旋转后与目标矩阵相同。rightThrice: 是否矩阵经过 270 度旋转后与目标矩阵相同。
双重循环遍历矩阵
通过双重循环遍历矩阵
mat和target,对比每个元素。 对于每个元素,检查它是否在四种旋转状态下匹配目标矩阵的对应元素。检查四种旋转
- 不旋转:
- 检查原始矩阵
mat[i][j]与目标矩阵target[i][j]是否相同。
- 检查原始矩阵
- 右旋 90 度:
- 旋转 90 度后,第
i行第j列的元素会变成原矩阵第j行第n-1-i列的元素。 - 检查原始矩阵
mat[i][j]与目标矩阵target[j][n - 1 - i]是否相同。
- 旋转 90 度后,第
- 右旋 180 度:
- 旋转 180 度后的元素位置是
target[m - 1 - i][n - 1 - j]。 - 检查原始矩阵
mat[i][j]与目标矩阵target[j][n - 1 - i]是否相同。
- 旋转 180 度后的元素位置是
- 右旋 270 度:
- 旋转 270 度后的元素位置是
target[m - 1 - j][i]。 - 检查原始矩阵
mat[i][j]与目标矩阵target[j][n - 1 - i]是否相同。
- 旋转 270 度后的元素位置是
- 不旋转:
提前退出优化
如果在某次循环中,四种旋转都没有匹配,即
normal、rightOnce、rightTwice和rightThrice都为false,表示mat无论如何旋转都无法匹配target,那么可以直接返回false,避免继续遍历。返回结果 如果四种旋转中至少有一种情况匹配成功,则返回
true,表示mat可以通过旋转与target匹配。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
O(m * n),其中m和n是矩阵的行和列数,需要遍历每个元素四次进行比较。空间复杂度:
O(1),只使用了常数空间来存储标志位。
代码
/**
* @param {number[][]} mat
* @param {number[][]} target
* @return {boolean}
*/
var findRotation = function (mat, target) {
const m = mat.length;
const n = mat[0].length;
let normal = true;
let rightOnce = true;
let rightTwice = true;
let rightThrice = true;
// 遍历矩阵,逐个检查四种旋转情况
for (let i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < n; j++) {
// 不旋转 mat
if (normal && mat[i][j] !== target[i][j]) {
normal = false;
}
// mat 右旋 90 度
if (rightOnce && mat[i][j] !== target[j][n - 1 - i]) {
rightOnce = false;
}
// mat 右旋 180 度
if (rightTwice && mat[i][j] !== target[m - 1 - i][n - 1 - j]) {
rightTwice = false;
}
// mat 右旋 270 度
if (rightThrice && mat[i][j] !== target[m - 1 - j][i]) {
rightThrice = false;
}
// 如果四种情况都不符合,提前返回 false
if (!normal && !rightOnce && !rightTwice && !rightThrice) {
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
};
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 48 | 旋转图像 | [✓] | 数组 数学 矩阵 | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
