173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
173. Binary Search Tree Iterator
🟠 🔖 栈 树 设计 二叉搜索树 二叉树 迭代器 🔗 LeetCode
题目
Implement the BSTIterator class that represents an iterator over the in-order traversal of a binary search tree (BST):
BSTIterator(TreeNode root)Initializes an object of theBSTIteratorclass. Therootof the BST is given as part of the constructor. The pointer should be initialized to a non-existent number smaller than any element in the BST.boolean hasNext()Returnstrueif there exists a number in the traversal to the right of the pointer, otherwise returnsfalse.int next()Moves the pointer to the right, then returns the number at the pointer.
Notice that by initializing the pointer to a non-existent smallest number, the first call to next() will return the smallest element in the BST.
You may assume that next() calls will always be valid. That is, there will be at least a next number in the in-order traversal when next() is called.
Example 1:
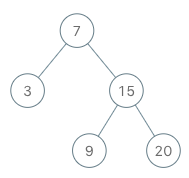
Input
["BSTIterator", "next", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext", "next", "hasNext"]
[[[7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], [], []]
Output
[null, 3, 7, true, 9, true, 15, true, 20, false]
Explanation
BSTIterator bSTIterator = new BSTIterator([7, 3, 15, null, null, 9, 20]);
bSTIterator.next(); // return 3
bSTIterator.next(); // return 7
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True
bSTIterator.next(); // return 9
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True
bSTIterator.next(); // return 15
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return True
bSTIterator.next(); // return 20
bSTIterator.hasNext(); // return False
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 105]. 0 <= Node.val <= 10^6- At most
105calls will be made tohasNext, andnext.
Follow up:
- Could you implement
next()andhasNext()to run in averageO(1)time and useO(h)memory, wherehis the height of the tree?
题目大意
实现一个二叉搜索树迭代器。你将使用二叉搜索树的根节点初始化迭代器,调用 next() 将返回二叉搜索树中的下一个最小的数,调用 hasNext() 将返回二叉搜索树中是否存在下一个数。
解题思路
可以采用中序遍历的方式,通过队列来模拟递归过程。
因为题目要求调用 next() 返回下一个最小的数,即按照从小到大的顺序返回元素,这正好符合二叉搜索树中序遍历的特性,中序遍历会按照升序访问二叉搜索树的节点。
代码
class BSTIterator {
// @param {TreeNode} root
constructor(root) {
this.queue = [];
this._inorder(root);
}
// 中序遍历
_inorder(root) {
if (!root) return null;
this._inorder(root.left);
this.queue.push(root.val);
this._inorder(root.right);
}
// @return {number}
next() {
return this.queue.shift();
}
// @return {boolean}
hasNext() {
return this.queue.length > 0;
}
}
相关题目
- [94. 二叉树的中序遍历](./0094.md)
- [🔒 Flatten 2D Vector](https://leetcode.com/problems/flatten-2d-vector)
- [🔒 Zigzag Iterator](https://leetcode.com/problems/zigzag-iterator)
- [284. 顶端迭代器](https://leetcode.com/problems/peeking-iterator)
- [🔒 Inorder Successor in BST](https://leetcode.com/problems/inorder-successor-in-bst)
- [🔒 Binary Search Tree Iterator II](https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-search-tree-iterator-ii)
