117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
117. Populating Next Right Pointers in Each Node II
🟠 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 广度优先搜索 链表 二叉树 🔗 LeetCode
题目
Given a binary tree
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
Populate each next pointer to point to its next right node. If there is no next right node, the next pointer should be set to NULL.
Initially, all next pointers are set to NULL.
Example 1:
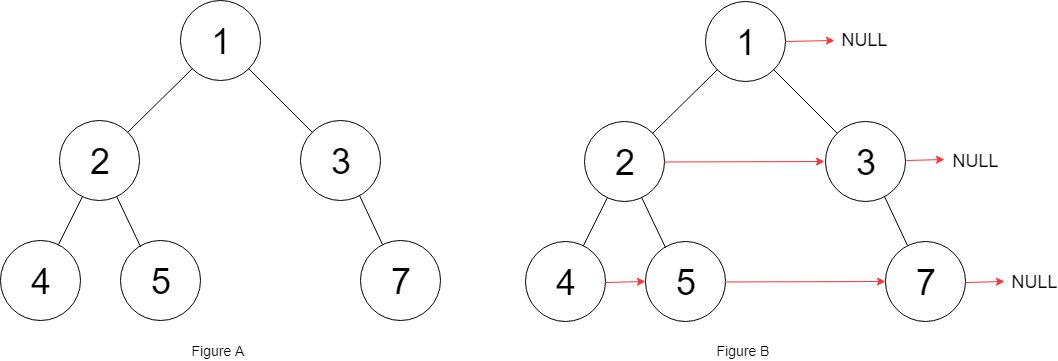
Input: root = [1,2,3,4,5,null,7]
Output: [1,#,2,3,#,4,5,7,#]
Explanation: Given the above binary tree (Figure A), your function should populate each next pointer to point to its next right node, just like in Figure B. The serialized output is in level order as connected by the next pointers, with '#' signifying the end of each level.
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 6000]. -100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow-up:
- You may only use constant extra space.
- The recursive approach is fine. You may assume implicit stack space does not count as extra space for this problem.
题目大意
给定一个二叉树:
struct Node {
int val;
Node *left;
Node *right;
Node *next;
}
填充它的每个 next 指针,让这个指针指向其下一个右侧节点。如果找不到下一个右侧节点,则将 next 指针设置为 NULL。初始状态下,所有 next 指针都被设置为 NULL。
你只能使用常量级额外空间。 使用递归解题也符合要求,本题中递归程序的隐式栈空间不计入额外空间复杂度。
解题思路
和 第 116 题 一样,本质上是二叉树的层序遍历,基于广度优先搜索,将每层的节点放入队列,并遍历队列进行连接。
代码
/**
* @param {Node} root
* @return {Node}
*/
var connect = function (root) {
if (!root) return root;
let queue = [root];
while (queue.length) {
let len = queue.length;
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i + 1 < len) queue[i].next = queue[i + 1];
if (queue[i].left) queue.push(queue[i].left);
if (queue[i].right) queue.push(queue[i].right);
}
queue = queue.slice(len);
}
return root;
};
