2017. 网格游戏
2017. 网格游戏
题目
You are given a 0-indexed 2D array grid of size 2 x n, where grid[r][c] represents the number of points at position (r, c) on the matrix. Two robots are playing a game on this matrix.
Both robots initially start at (0, 0) and want to reach (1, n-1). Each robot may only move to the right ((r, c) to (r, c + 1)) or down((r, c) to (r + 1, c)).
At the start of the game, the first robot moves from (0, 0) to (1, n-1), collecting all the points from the cells on its path. For all cells (r, c) traversed on the path, grid[r][c] is set to 0. Then, the second robot moves from (0, 0) to (1, n-1), collecting the points on its path. Note that their paths may intersect with one another.
The first robot wants to minimize the number of points collected by the second robot. In contrast, the second robot wants to maximize the number of points it collects. If both robots play optimally , return thenumber of points collected by the second robot.
Example 1:
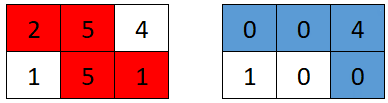
Input: grid = [[2,5,4],[1,5,1]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The optimal path taken by the first robot is shown in red, and the optimal path taken by the second robot is shown in blue.
The cells visited by the first robot are set to 0.
The second robot will collect 0 + 0 + 4 + 0 = 4 points.
Example 2:
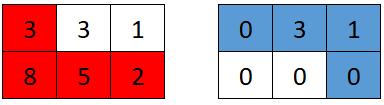
Input: grid = [[3,3,1],[8,5,2]]
Output: 4
Explanation: The optimal path taken by the first robot is shown in red, and the optimal path taken by the second robot is shown in blue.
The cells visited by the first robot are set to 0.
The second robot will collect 0 + 3 + 1 + 0 = 4 points.
Example 3:
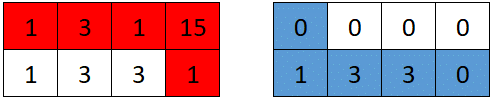
Input: grid = [[1,3,1,15],[1,3,3,1]]
Output: 7
Explanation: The optimal path taken by the first robot is shown in red, and the optimal path taken by the second robot is shown in blue.
The cells visited by the first robot are set to 0.
The second robot will collect 0 + 1 + 3 + 3 + 0 = 7 points.
Constraints:
grid.length == 2n == grid[r].length1 <= n <= 5 * 10^41 <= grid[r][c] <= 10^5
题目大意
给你一个下标从 0 开始的二维数组 grid ,数组大小为 2 x n ,其中 grid[r][c] 表示矩阵中 (r, c) 位置上的点数。现在有两个机器人正在矩阵上参与一场游戏。
两个机器人初始位置都是 (0, 0) ,目标位置是 (1, n-1) 。每个机器人只会 向右 ((r, c) 到 (r, c + 1)) 或 向下((r, c) 到 (r + 1, c)) 。
游戏开始,第一个 机器人从 (0, 0) 移动到 (1, n-1) ,并收集路径上单元格的全部点数。对于路径上所有单元格 (r, c) ,途经后 grid[r][c] 会重置为 0 。然后,第二个 机器人从 (0, 0) 移动到 (1, n-1) ,同样收集路径上单元的全部点数。注意,它们的路径可能会存在相交的部分。
第一个 机器人想要打击竞争对手,使 第二个 机器人收集到的点数 最小化 。与此相对,第二个 机器人想要 最大化 自己收集到的点数。两个机器人都发挥出自己的 最佳水平 的前提下,返回 第二个 机器人收集到的 点数 。
示例 1:

输入: grid = [[2,5,4],[1,5,1]]
输出: 4
解释: 第一个机器人的最佳路径如红色所示,第二个机器人的最佳路径如蓝色所示。
第一个机器人访问过的单元格将会重置为 0 。
第二个机器人将会收集到 0 + 0 + 4 + 0 = 4 个点。
示例 2:

输入: grid = [[3,3,1],[8,5,2]]
输出: 4
解释: 第一个机器人的最佳路径如红色所示,第二个机器人的最佳路径如蓝色所示。
第一个机器人访问过的单元格将会重置为 0 。
第二个机器人将会收集到 0 + 3 + 1 + 0 = 4 个点。
示例 3:

输入: grid = [[1,3,1,15],[1,3,3,1]]
输出: 7
解释: 第一个机器人的最佳路径如红色所示,第二个机器人的最佳路径如蓝色所示。
第一个机器人访问过的单元格将会重置为 0 。
第二个机器人将会收集到 0 + 1 + 3 + 3 + 0 = 7 个点。
提示:
grid.length == 2n == grid[r].length1 <= n <= 5 * 10^41 <= grid[r][c] <= 10^5
解题思路
玩家 1 选择路径后,玩家 2 需要选择一条与玩家 1 路径不重叠的路径。
玩家 2 的路径只能走玩家 1 路径的剩余部分(上行或下行),因此我们只需计算玩家 2 在这两种情况下的分数即可。
使用前缀和计算两个方向的路径和:
firstRowSum表示玩家 1 从当前列之后(包括当前列)向右的总和。secondRowSum表示玩家 1 从当前列之前(不包括当前列)向左的总和。
遍历每个列,假设玩家 1 切换路径的分割点为当前列
i,计算以下两种情况的分数:- 玩家 2 向右选择剩余的第一行路径分数(
firstRowSum)。 - 玩家 2 向左选择第二行路径分数(
secondRowSum)。
- 玩家 2 向右选择剩余的第一行路径分数(
对于每一列,玩家 2 的分数是
max(firstRowSum, secondRowSum)(即选择路径时的最坏情况),我们需要找到这种分数的最小值。
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),其中n是列数,遍历一遍网格的列。 - 空间复杂度:
O(1),使用常数级变量。
代码
/**
* @param {number[][]} grid
* @return {number}
*/
var gridGame = function (grid) {
let firstRowSum = grid[0].reduce((a, b) => a + b, 0); // 第一行总和
let secondRowSum = 0; // 第二行初始累积和
let minSum = Infinity; // 玩家 2 的最小可能分数
for (let i = 0; i < grid[0].length; i++) {
firstRowSum -= grid[0][i]; // 从第一行总和中减去当前列的值
minSum = Math.min(minSum, Math.max(firstRowSum, secondRowSum)); // 玩家 2 的最大分数(选择最优路径)
secondRowSum += grid[1][i]; // 累加第二行的值
}
return minSum;
};
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2483 | 商店的最少代价 | 字符串 前缀和 | 🟠 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
