1028. 从先序遍历还原二叉树
1028. 从先序遍历还原二叉树
🔴 🔖 树 深度优先搜索 字符串 二叉树 🔗 力扣 LeetCode
题目
We run a preorder depth-first search (DFS) on the root of a binary tree.
At each node in this traversal, we output D dashes (where D is the depth of this node), then we output the value of this node. If the depth of a node is D, the depth of its immediate child is D + 1. The depth of the root node is 0.
If a node has only one child, that child is guaranteed to be the left child.
Given the output traversal of this traversal, recover the tree and return its root.
Example 1:
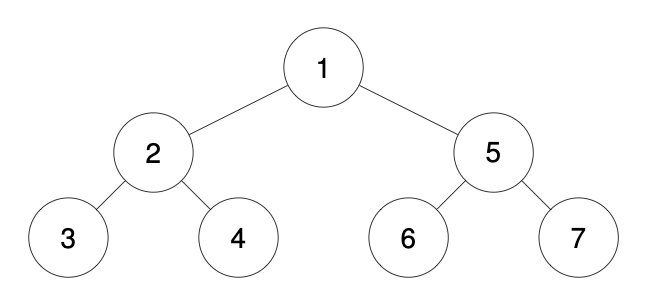
Input: traversal = "1-2--3--4-5--6--7"
Output: [1,2,5,3,4,6,7]
Example 2:
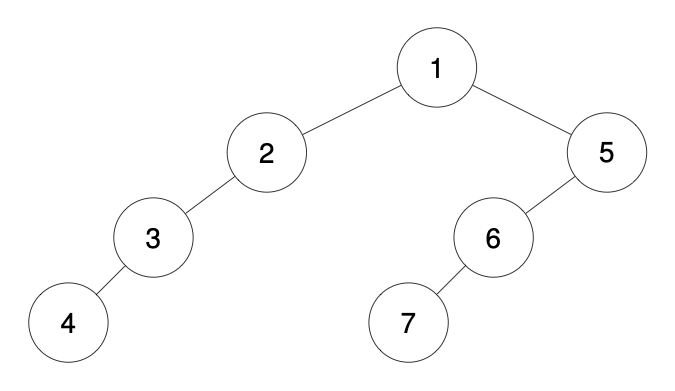
Input: traversal = "1-2--3---4-5--6---7"
Output: [1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]
Example 3:
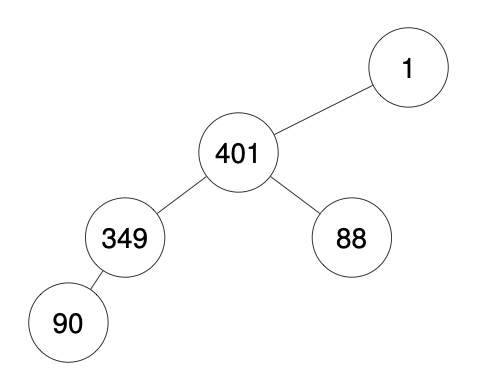
Input: traversal = "1-401--349---90--88"
Output: [1,401,null,349,88,90]
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the original tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 1 <= Node.val <= 10^9
题目大意
我们从二叉树的根节点 root 开始进行深度优先搜索。
在遍历中的每个节点处,我们输出 D 条短划线(其中 D 是该节点的深度),然后输出该节点的值。( 如果节点的深度为D,则其直接子节点的深度为 D + 1。根节点的深度为 0)。
如果节点只有一个子节点,那么保证该子节点为左子节点。
给出遍历输出 S,还原树并返回其根节点 root。
示例 1:

输入: "1-2--3--4-5--6--7"
输出:[1,2,5,3,4,6,7]
示例 2:

输入: "1-2--3---4-5--6---7"
输出:[1,2,5,3,null,6,null,4,null,7]
示例 3:

输入: "1-401--349---90--88"
输出:[1,401,null,349,88,90]
提示:
- 原始树中的节点数介于
1和1000之间。 - 每个节点的值介于
1和10 ^ 9之间。
解题思路
解析
traversal字符串traversal由-和数字组成,其中-的数量表示当前节点的深度,数字表示节点的值。- 依次遍历
traversal,解析每个节点的 深度 和 值。
使用栈来维护树的构造
- 栈
stack维护当前路径上的所有节点,stack[i]代表深度为i的节点。 - 遇到新的节点时:
- 先计算
depth(连续-的个数)。 - 解析
num(连续数字组成的值)。 - 根据
depth确定其父节点,并加入到对应的left或right位置。
- 先计算
- 栈
构造树
- 当
stack.length > depth时,说明当前节点的深度比栈顶小或相等,需要回溯到正确的父节点(即stack[depth - 1])。 - 将新节点加入到
stack[depth - 1]的left或right子节点。 - 最后将新节点入栈。
- 当
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:
O(n),每个字符只会被遍历一次。 - 空间复杂度:
O(n),最坏情况下栈存储n个节点。
代码
/**
* @param {string} traversal
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var recoverFromPreorder = function (traversal) {
const n = traversal.length;
let stack = [];
let i = 0;
while (i < n) {
let depth = 0;
while (i < n && traversal[i] === '-') {
depth++;
i++;
}
let num = 0;
while (i < n && traversal[i] >= '0' && traversal[i] <= '9') {
num = num * 10 + Number(traversal[i++]);
}
let node = new TreeNode(num);
while (stack.length > depth) {
stack.pop();
}
if (stack.length > 0) {
if (!stack[stack.length - 1].left) {
stack[stack.length - 1].left = node;
} else {
stack[stack.length - 1].right = node;
}
}
stack.push(node);
}
return stack[0];
};
