8. 实现 useState
8. 实现 useState
1. 支持 FuctionComponent
上一节我们实现了简单版的 react-dom 包,支持了首屏渲染触发更新,而 React 还有很多触发更新的方式,如类组件的 this.setState()、函数组件的 useState useEffect,这一节我们来实现函数组件的 useState。
useState 是 React 中的一个 Hook,React Hooks 是 React 16.8 引入的一项特性,目的是让你在函数组件中使用状态和其他 React 特性,以替代类组件中的状态和生命周期方法。在函数组件中使用 Hooks 有一些规则和限制:
- 只能在函数组件中调用 Hooks: Hooks 依赖于 React 的函数组件机制,所以只能在函数组件中使用,而不能在类组件中使用。如果你需要在类组件中使用类似的功能,可以考虑使用 React 的类组件生命周期方法和状态管理机制。
- 只能在顶层调用 Hooks: 不可以在条件语句、循环语句或嵌套函数中调用 Hooks。这确保 React 能够按照相同的顺序调用 Hooks,以确保状态之间的关系保持一致。
首先,我们需要将函数组件 FunctionComponent 加入到更新流程里面去,和 HostComponet、HostText 一样,FunctionComponent 的更新流程同样根植于 beginWork 和 completeWork 函数。
先在 beginWork 函数中增加 FunctionComponent 的情况判断,若 FiberNode 是函数组件,就调用 updateFunctionComponent 函数;
// packages/react-reconciler/src/beginWork.ts
// 比较并返回子 FiberNode
export const beginWork = (workInProgress: FiberNode) => {
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case HostRoot:
return updateHostRoot(workInProgress);
case HostComponent:
return updateHostComponent(workInProgress);
case FunctionComponent:
return updateFunctionComponent(workInProgress);
case HostText:
return updateHostText();
default:
if (__DEV__) {
console.warn('beginWork 未实现的类型', workInProgress.tag);
}
break;
}
};
updateFunctionComponent函数会调用函数组件本身来获取其返回的 React 元素树,例如函数组件 function App() { return 123 },只需调用 App() 就可以得到其子节点,进而将子节点传给 reconcileChildren 协调处理子节点的更新逻辑;
// packages/react-reconciler/src/beginWork.ts
function updateFunctionComponent(workInProgress: FiberNode) {
const nextChildren = renderWithHooks(workInProgress);
reconcileChildren(workInProgress, nextChildren);
return workInProgress.child;
}
调用函数组件的工作由 renderWithHooks 负责,函数保存在 FiberNode 的 type 字段中,因此只需要取出 type 字段执行以下即可得到其子节点;
// packages/react-reconciler/src/fiberHooks.ts
// 执行函数组件中的函数
export function renderWithHooks(workInProgress: FiberNode) {
// 函数保存在 type 字段中
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const props = workInProgress.pendingProps;
// 执行函数
const children = Component(props);
return children;
}
同样,在 completeWork 函数中增加 FunctionComponent 的情况判断,和 HostRoot 一样,不需要做其他的处理,直接向上冒泡即可;
// packages/react-reconciler/src/completeWork.ts
// 生成更新计划,计算和收集更新 flags
export const completeWork = (workInProgress: FiberNode) => {
const newProps = workInProgress.pendingProps;
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
switch (workInProgress.tag) {
case HostRoot:
case FunctionComponent:
bubbleProperties(workInProgress);
return null;
// ...
这样,我们就实现了 FunctionComponent 的基本功能。
2. 实现共享数据层
我们知道 Hooks 只能在函数组件中调用,若我们在一个 Hook 的回调函数中调用另一个 Hook 会报错,类似下面这样:
function App() {
useEffect(() => {
useState(1)
}
}
那 Hooks 如何感知被调用的上下文环境呢?
方法是在不同上下文中,调用的 Hooks 不是同一个函数。在 mount 时、update 时、以及其它上下文中,分别实现不同的 Hooks 函数,从而确保 Hooks 在正确的上下文环境中执行。
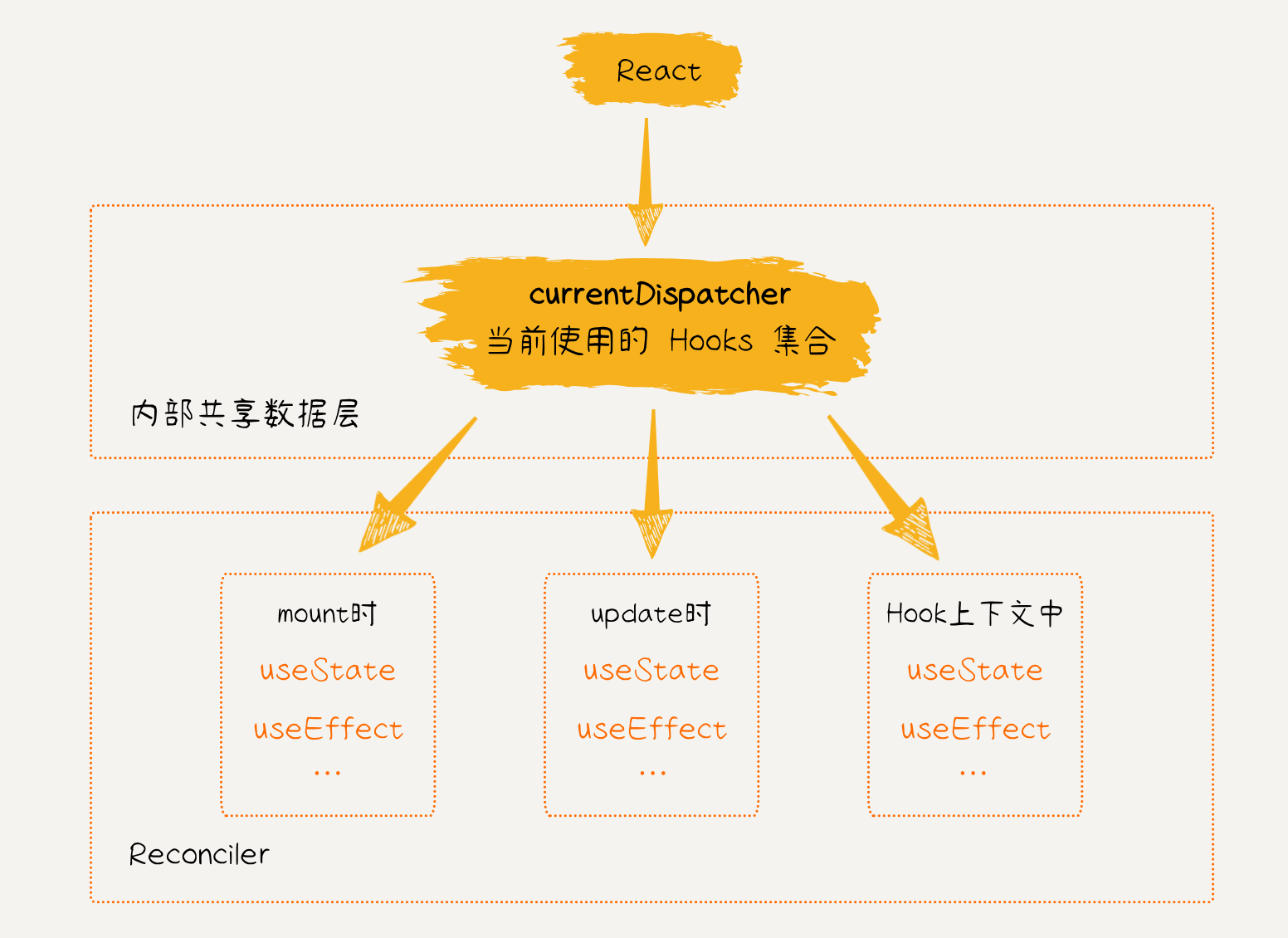
我们调用useState 时的一般语法是:
import { useState } from 'react';
const [state, setState] = useState(initialState);
可以看出,useState 是被 react 包导出,而要想感知上下文环境,则需要依赖 react-reconciler 包中的更新流程,也就是说两个包之间需要共享数据,因此就需要实现一个内部数据共享层(ReactSharedInternals)。
先在 react 包中新建一个 currentDispatcher.ts 文件,里面保存了当前使用的 Hooks 指针 currentDispatcher,同时导出一个 resolveDispatcher 函数,方便查询当前使用的 Hooks 集合:
// packages/react/src/currentDispatcher.ts
import { Action } from 'shared/ReactTypes';
// const [data, setData] = useState(0);
// or
// const [data, setData] = useState(0data) => data + 1);
export interface Dispatcher {
useState: <S>(initialState: (() => S) | S) => [S, Dispatch<S>];
}
export type Dispatch<State> = (action: Action<State>) => void;
const currentDispatcher: { current: Dispatcher | null } = {
current: null
};
export const resolveDispatcher = (): Dispatcher => {
const dispatcher = currentDispatcher.current;
if (dispatcher == null) {
throw new Error('Hooks 只能在函数组件中执行');
}
return dispatcher;
};
export default currentDispatcher;
接着,在react/index.ts 中对外暴露 useState 函数,这个函数返回的是 currentDispatcher.current.useState;
同事将内部共享数据层暴露出去,里面包含了 currentDispatcher 的数据。React 官方为内部共享数据层取了一个很长的名字,以警告开发者不要随便修改里面的数据:
__SECRET_INTERNALS_DO_NOT_USE_OR_YOU_WILL_BE_FIRED。
// packages/react/index.ts
import currentDispatcher, {
Dispatcher,
resolveDispatcher
} from './src/currentDispatcher';
import { jsx } from './src/jsx';
export const useState: Dispatcher['useState'] = (initialState) => {
const dispatcher = resolveDispatcher();
return dispatcher.useState(initialState);
};
// 内部数据共享层
export const __SECRET_INTERNALS_DO_NOT_USE_OR_YOU_WILL_BE_FIRED = {
currentDispatcher
};
export default {
version: '1.0.0',
createElement: jsx
};
为了将 react-reconciler 包和 react 包解耦,我们不直接从react 包中调用数据共享层,而是通过 shared 包中转一下:
// packages/shared/internals.ts
import * as React from 'react';
// 为了将 react-reconciler 和 react 解耦,在 shared 中转,方便 react-reconciler 使用
const internals = React.__SECRET_INTERNALS_DO_NOT_USE_OR_YOU_WILL_BE_FIRED;
export default internals;
现在,我们就可以在 react 包通过数据共享层获取当前的上下文环境,并返回不同的 Hooks 集合了,接下来,我们需要在 react-reconciler 包中实现对应不同上下文环境的 Hooks 集合。
3. 实现 useState
前面我们提到,在 beginWork 阶段,为了获取函数组件的 children,在 updateFunctionComponent 函数中会调用 renderWithHooks 方法。renderWithHooks 方法会调用函数组件,并在执行的过程中,执行相应的 hook 方法。
因此,我们需要在 renderWithHooks 方法中判断当前的上下文环境,来决定要调用哪个 Hooks 集合,判断的方法是根据 workInProgress.alternate:
- 若它为
null,代表此时还没有真实 DOM 树(首屏还没有渲染),所以是 mount 阶段,应该调用 mount 阶段对应的 Hooks 集合:HooksDispatcherOnMount,将它赋值给currentDispatcher; - 否则就是 update 阶段,应该调用 update 阶段对应的 Hooks 集合:
HooksDispatcherOnUpdate
// packages/react-reconciler/src/fiberHooks.ts
// ...
import internals from 'shared/internals';
const { currentDispatcher } = internals;
// 执行函数组件中的函数
export function renderWithHooks(workInProgress: FiberNode) {
// 赋值
currentlyRenderingFiber = workInProgress;
workInProgress.memoizedState = null;
// 判断 Hooks 被调用的时机
const current = workInProgress.alternate;
if (current !== null) {
// 组件的更新阶段(update)
currentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnUpdate;
} else {
// 首屏渲染阶段(mount)
currentDispatcher.current = HooksDispatcherOnMount;
}
// 函数保存在 type 字段中
const Component = workInProgress.type;
const props = workInProgress.pendingProps;
// 执行函数
const children = Component(props);
// 重置
currentlyRenderingFiber = null;
workInProgressHook = null;
return children;
}
const HooksDispatcherOnMount: Dispatcher = {
useState: mountState
};
const HooksDispatcherOnUpdate: Dispatcher = {
useState: updateState
};
其中,currentlyRenderingFiber 是一个全局变量,用于跟踪当前正在被处理的 FiberNode 节点,以便在调用 Hooks 时能找到正确的 FiberNode 节点,将状态和上下文与之相关联。workInProgressHook 也是一个全局变量,用于跟踪当前正在进行工作的 Hook。
接着,我们来实现 mount 阶段对应的 useState 方法:mountState,先定义一下 Hook 的数据结构:
// 定义 Hook 数据结构
export interface Hook {
memoizedState: any; // 保存 Hook 的数据
queue: any;
next: Hook | null;
}
注意,Hook 和 FiberNode 都有 memoizedState 字段,但是二者的含义不一样,两者的关系如下图:
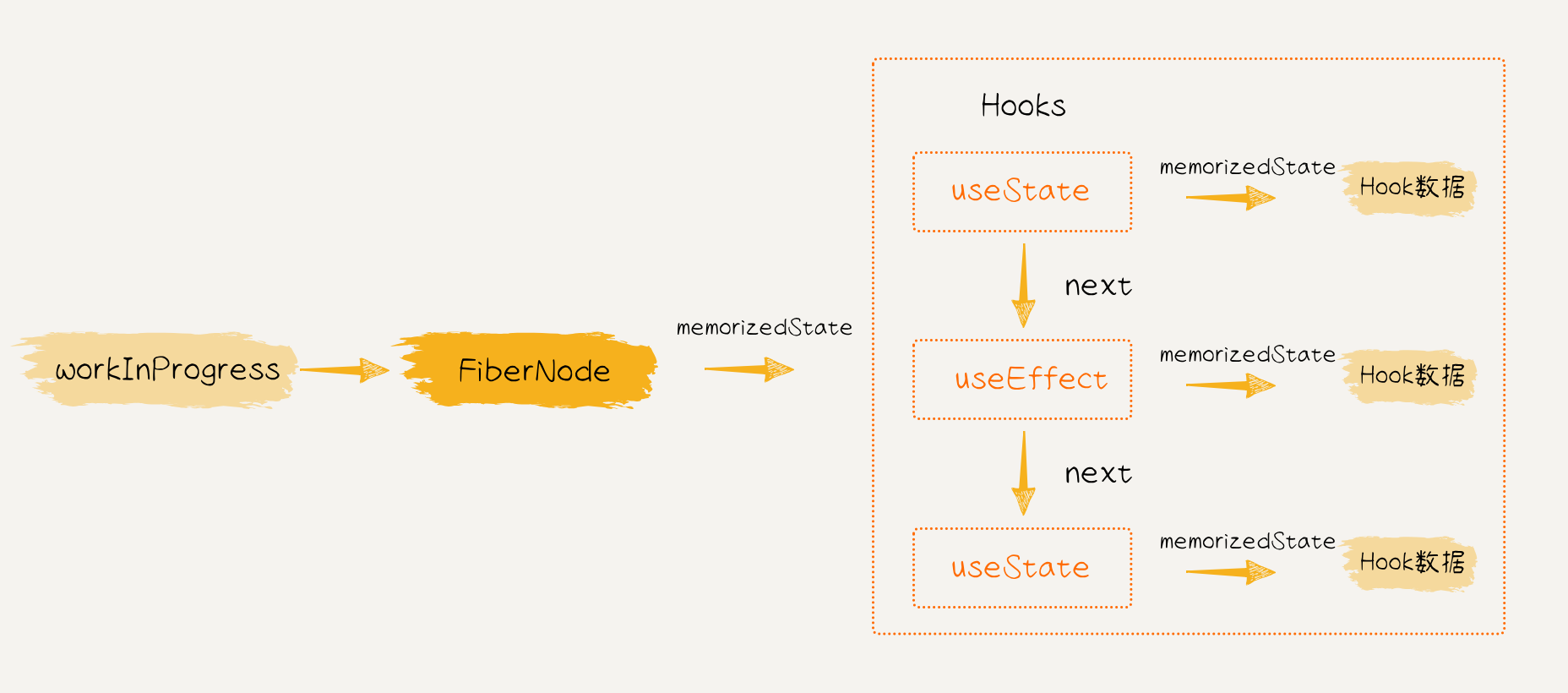
在 Reconciler 更新流程中,会遍历 Fiber 树,而 workInProgress 字段指向了当前正在被执行的 FiberNode 节点,该节点的 memoizedState 字段中保存着待执行的 Hooks 链表;链表中的每个 Hook 通过 next 指针连接在一起,每个 Hook 都有一个 memoizedState 字段,指向了对应的 Hook 数据。
接着实现 mountState,现在需要做两件事:
- 从 Hooks 链表中获取当前正在工作的
useState - 获取当前
useState对应的 Hook 数据
实现 mountWorkInProgressHook 函数,负责从 Hooks 链表中获取当前正在工作的 Hook。对于 mount 阶段,我们需要新建一个 Hook,然后将它赋值给 workInProgressHook 变量,这个变量的含义就是当前正在工作的 Hook,同时还需要注意,Hooks 是一个链表,链表中的每个 Hook 通过 next 指针连接在一起,所以要维护好 next 指针。
// 获取当前正在工作的 Hook
function mountWorkInProgressHook(): Hook {
const hook: Hook = {
memoizedState: null,
queue: null,
next: null
};
if (workInProgressHook == null) {
// mount 时的第一个hook
if (currentlyRenderingFiber !== null) {
workInProgressHook = hook;
currentlyRenderingFiber.memoizedState = workInProgressHook;
} else {
// currentlyRenderingFiber == null 代表 Hook 执行的上下文不是一个函数组件
throw new Error('Hooks 只能在函数组件中执行');
}
} else {
// mount 时的其他 hook
// 将当前工作的 Hook 的 next 指向新建的 hook,形成 Hooks 链表
workInProgressHook.next = hook;
// 更新当前工作的 Hook
workInProgressHook = hook;
}
return workInProgressHook;
}
对于 mount 阶段来说,当前 useState 对应的 Hook 数据就是 initialState,我们需要将这个数据存放在 Hook 的 memoizedState 变量中。另外,因为 useState 可以触发更新,所以我们创建一个 UpdateQueue,存放在 Hook 的 queue 变量中。
function mountState<State>(
initialState: (() => State) | State
): [State, Dispatch<State>] {
// 当前正在工作的 useState
const hook = mountWorkInProgressHook();
// 当前 useState 对应的 Hook 数据
let memoizedState;
if (initialState instanceof Function) {
memoizedState = initialState();
} else {
memoizedState = initialState;
}
hook.memoizedState = memoizedState;
const queue = createUpdateQueue<State>();
hook.queue = queue;
// 实现 dispatch
const dispatch = dispatchSetState.bind(null, currentlyRenderingFiber, queue);
queue.dispatch = dispatch;
return [memoizedState, dispatch];
}
最后我们还要实现 useState 的 dispatch 方法,并接入当前的更新流程。
// 用于触发状态更新的逻辑
function dispatchSetState<State>(
fiber: FiberNode,
updateQueue: UpdateQueue<State>,
action: Action<State>
) {
const update = createUpdate(action);
enqueueUpdate(updateQueue, update);
// 调度更新
scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber);
}
至此,我们就实现了函数组件中的 useState 方法,但是 useState 的 dispatch 还没有完全实现,因为我们还没有实现 update 流程,如:删除节点、更新节点等,这些功能将在 第 10 节 中实现。
相关代码可在 git tag v1.8 查看,地址:https://github.com/2xiao/my-react/tree/v1.8
