2872. 可以被 K 整除连通块的最大数目
2872. 可以被 K 整除连通块的最大数目
题目
There is an undirected tree with n nodes labeled from 0 to n - 1. You are given the integer n and a 2D integer array edges of length n - 1, where edges[i] = [ai, bi] indicates that there is an edge between nodes ai and bi in the tree.
You are also given a 0-indexed integer array values of length n, where values[i] is the value associated with the ith node, and an integer k.
A valid split of the tree is obtained by removing any set of edges, possibly empty, from the tree such that the resulting components all have values that are divisible by k, where the value of a connected component is the sum of the values of its nodes.
Return the maximum number of components in any valid split.
Example 1:
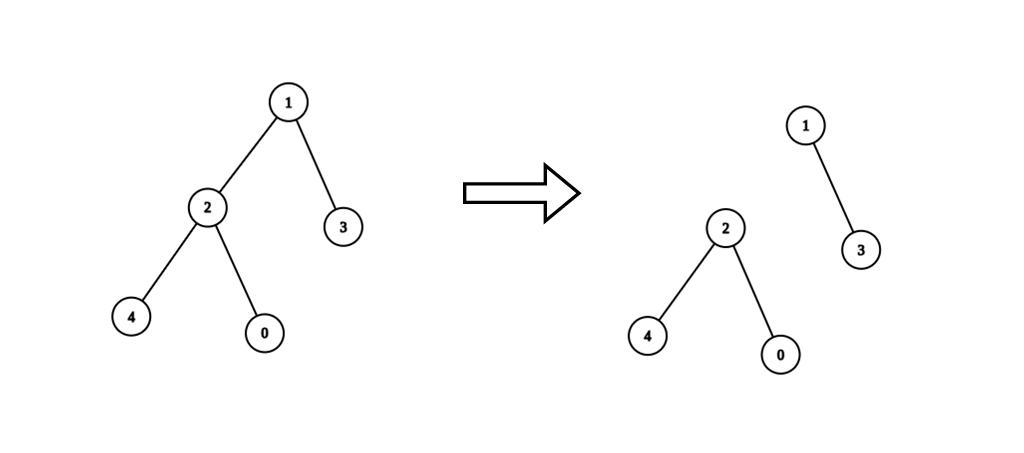
Input: n = 5, edges = [[0,2],[1,2],[1,3],[2,4]], values = [1,8,1,4,4], k = 6
Output: 2
Explanation: We remove the edge connecting node 1 with 2. The resulting split is valid because:
- The value of the component containing nodes 1 and 3 is values[1] + values[3] = 12.
- The value of the component containing nodes 0, 2, and 4 is values[0] + values[2] + values[4] = 6.
It can be shown that no other valid split has more than 2 connected components.
Example 2:
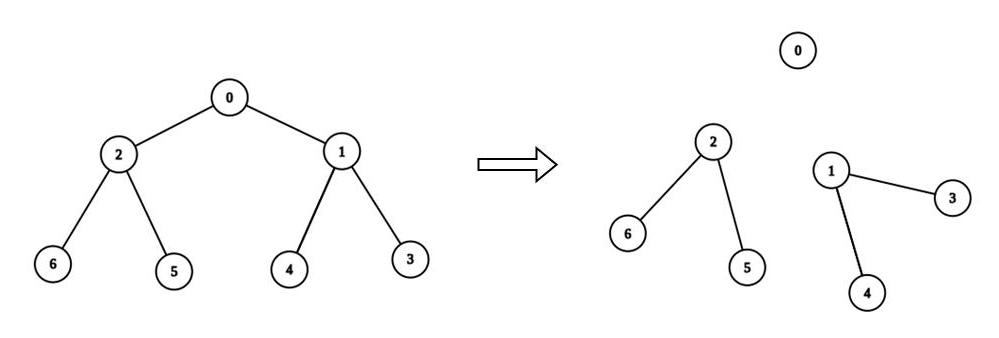
Input: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], values = [3,0,6,1,5,2,1], k = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: We remove the edge connecting node 0 with 2, and the edge connecting node 0 with 1. The resulting split is valid because:
- The value of the component containing node 0 is values[0] = 3.
- The value of the component containing nodes 2, 5, and 6 is values[2] + values[5] + values[6] = 9.
- The value of the component containing nodes 1, 3, and 4 is values[1] + values[3] + values[4] = 6.
It can be shown that no other valid split has more than 3 connected components.
Constraints:
1 <= n <= 3 * 10^4edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nvalues.length == n0 <= values[i] <= 10^91 <= k <= 10^9- Sum of
valuesis divisible byk. - The input is generated such that
edgesrepresents a valid tree.
题目大意
给你一棵 n 个节点的无向树,节点编号为 0 到 n - 1 。给你整数 n 和一个长度为 n - 1 的二维整数数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示树中节点 ai 和 bi 有一条边。
同时给你一个下标从 0 开始长度为 n 的整数数组 values ,其中 values[i] 是第 i 个节点的 值 。再给你一个整数 k 。
你可以从树中删除一些边,也可以一条边也不删,得到若干连通块。一个 连通块的值 定义为连通块中所有节点值之和。如果所有连通块的值都可以被 k 整除,那么我们说这是一个 合法分割 。
请你返回所有合法分割中,连通块数目的最大值 。
示例 1:

输入: n = 5, edges = [[0,2],[1,2],[1,3],[2,4]], values = [1,8,1,4,4], k = 6
输出: 2
解释: 我们删除节点 1 和 2 之间的边。这是一个合法分割,因为:
- 节点 1 和 3 所在连通块的值为 values[1] + values[3] = 12 。
- 节点 0 ,2 和 4 所在连通块的值为 values[0] + values[2] + values[4] = 6 。
最多可以得到 2 个连通块的合法分割。
示例 2:

输入: n = 7, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,3],[1,4],[2,5],[2,6]], values = [3,0,6,1,5,2,1], k = 3
输出: 3
解释: 我们删除节点 0 和 2 ,以及节点 0 和 1 之间的边。这是一个合法分割,因为:
- 节点 0 的连通块的值为 values[0] = 3 。
- 节点 2 ,5 和 6 所在连通块的值为 values[2] + values[5] + values[6] = 9 。
- 节点 1 ,3 和 4 的连通块的值为 values[1] + values[3] + values[4] = 6 。
最多可以得到 3 个连通块的合法分割。
提示:
1 <= n <= 3 * 10^4edges.length == n - 1edges[i].length == 20 <= ai, bi < nvalues.length == n0 <= values[i] <= 10^91 <= k <= 10^9values之和可以被k整除。- 输入保证
edges是一棵无向树。
解题思路
这道题目可以通过树的深度优先搜索(DFS)来解决。
构建树的邻接表:
- 树是一个无向连通图,且没有环。
- 根据输入的
edges构造树的邻接表表示,以便我们可以通过 DFS 遍历整棵树。
DFS 遍历树:
- 我们可以任选一个节点(通常是节点
0)作为树的根,然后用 DFS 遍历整个树。 - 递归计算子树的节点值之和。
- 如果一个子树的节点和
sum可以被k整除,那么从该子树的根节点断开后,该子树本身就构成一个合法的连通块,增加连通块数量,同时从当前节点断开与其父节点的连接。
- 我们可以任选一个节点(通常是节点
计算最大连通块数量:
- 在 DFS 的过程中记录分割的次数,即合法连通块的数量。
- 返回结果为最大连通块数量。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
- 构建邻接表的时间复杂度为
O(n)。 - DFS 遍历树的时间复杂度为
O(n)。 - 总时间复杂度为
O(n)。
- 构建邻接表的时间复杂度为
空间复杂度:
- 邻接表占用
O(n)空间。 - 递归调用栈的深度为
O(n)(最坏情况下为链状树)。 - 总空间复杂度为
O(n)。
- 邻接表占用
代码
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @param {number[]} values
* @param {number} k
* @return {number}
*/
var maxKDivisibleComponents = function (n, edges, values, k) {
// 构建邻接表
const tree = Array.from({ length: n }, () => []);
for (const [a, b] of edges) {
tree[a].push(b);
tree[b].push(a);
}
let result = 0;
// 深度优先搜索
const dfs = (node, parent) => {
let sum = values[node]; // 当前子树的节点值之和
for (const neighbor of tree[node]) {
if (neighbor === parent) continue; // 跳过父节点
sum += dfs(neighbor, node); // 递归计算子树的和
}
// 如果当前子树和可以被 k 整除,则形成一个连通块
if (sum % k === 0) {
result++;
return 0; // 当前子树可以分割掉,返回 0
}
return sum; // 返回子树的和
};
// 从节点 0 开始 DFS
dfs(0, -1);
return result;
};
相关题目
| 题号 | 标题 | 题解 | 标签 | 难度 | 力扣 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2440 | 创建价值相同的连通块 | 树 深度优先搜索 数组 2+ | 🔴 | 🀄️ 🔗 |
