剑指 Offer II 31. 最近最少使用缓存
剑指 Offer II 31. 最近最少使用缓存
题目
Design a data structure that follows the constraints of a Least Recently Used (LRU) cache.
Implement the LRUCache class:
LRUCache(int capacity)Initialize the LRU cache with positive sizecapacity.int get(int key)Return the value of thekeyif the key exists, otherwise return1.void put(int key, int value)Update the value of thekeyif thekeyexists. Otherwise, add thekey-valuepair to the cache. If the number of keys exceeds thecapacityfrom this operation, evict the least recently used key.
Follow up:Could you do get and put in O(1) time complexity?
Example 1:
Input
["LRUCache", "put", "put", "get", "put", "get", "put", "get", "get", "get"]
[[2], [1, 1], [2, 2], [1], [3, 3], [2], [4, 4], [1], [3], [4]]
Output
[null, null, null, 1, null, -1, null, -1, 3, 4]
Explanation
LRUCache lRUCache = new LRUCache(2);
lRUCache.put(1, 1); // cache is {1=1}
lRUCache.put(2, 2); // cache is {1=1, 2=2}
lRUCache.get(1); // return 1
lRUCache.put(3, 3); // LRU key was 2, evicts key 2, cache is {1=1, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(2); // returns -1 (not found)
lRUCache.put(4, 4); // LRU key was 1, evicts key 1, cache is {4=4, 3=3}
lRUCache.get(1); // return -1 (not found)
lRUCache.get(3); // return 3
lRUCache.get(4); // return 4
Constraints:
1 <= capacity <= 30000 <= key <= 30000 <= value <= 10^4- At most
3 * 10^4calls will be made togetandput.
注意
本题与 LeetCode 第 146 题 相同。
题目大意
请你设计并实现一个满足 LRU (最近最少使用) 缓存 约束的数据结构。
实现 LRUCache 类:
LRUCache(int capacity)以 正整数 作为容量capacity初始化 LRU 缓存int get(int key)如果关键字 key 存在于缓存中,则返回关键字的值,否则返回-1。void put(int key, int value)如果关键字key已经存在,则变更其数据值value;如果不存在,则向缓存中插入该组key-value。如果插入操作导致关键字数量超过capacity,则应该 逐出 最久未使用的关键字。- 函数
get和put必须以O(1)的平均时间复杂度运行。
解题思路
LRU 是 Least Recently Used 的缩写,即最近最少使用,是一种常用的缓存淘汰算法,选择最久未使用的页面予以淘汰。
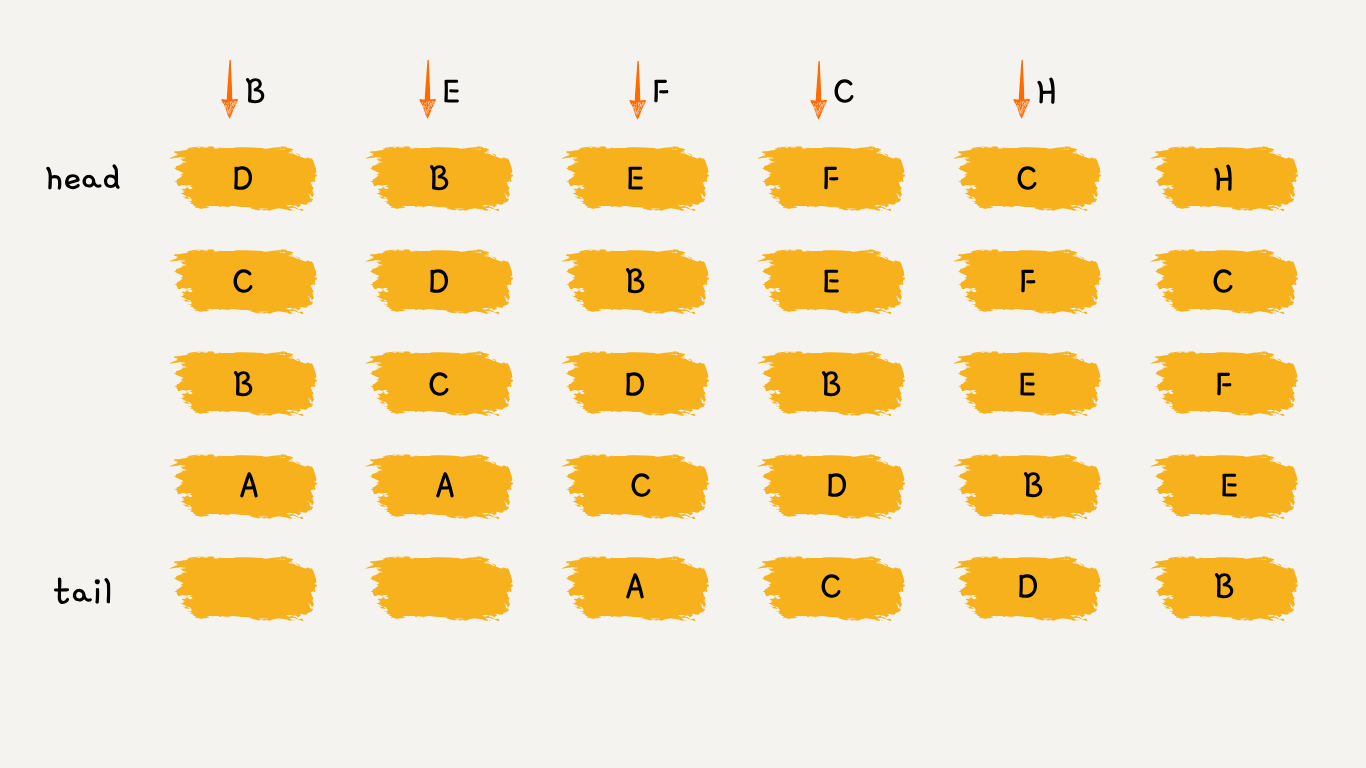
可以维护一个有序单链表,越靠近链表尾部的节点是越早之前访问的。如上图所示:
- 要插入 B 的时候,发现缓存中有 B ,这时需要把 B 放到链首,因为它被使用了;
- 要插入 E 的时候,缓存中没有 E,直接把 E 插入链首;
- 要插入 F 的时候,缓存中没有 F,容量已满,需要淘汰掉 A ,因为 A 最久未被使用;
- 要插入 C 的时候,发现缓存中有 C ,这时需要把 C 放到链首;
- 要插入 H 的时候,缓存中没有 H,容量已满,需要淘汰掉 D ,因为 D 最久未被使用;
可以发现,LRU 更新和插入新节点都发生在链首,删除数据都发生在链尾。
LRUCache 类有两个方法:
get当有一个新的数据被访问时:- 如果此数据之前已经被缓存在链表中了,遍历得到这个数据对应的节点,并将其从原来的位置删除,然后再插入到链表的头部,返回数据的值;
- 如果此数据没有在缓存链表中,则返回
-1;
put往链表里新增数据时:- 如果此数据之前已经被缓存在链表中了,更新此数据的值,并将其从原来的位置删除,再插入到链表的头部;
- 如果此数据没有在缓存链表中,又分为两种情况:
- 如果此时缓存未满,则将此节点直接插入到链表的头部;
- 如果此时缓存已满,则链表尾节点删除,将新的数据节点插入链表的头部。
这样就用链表实现了一个 LRU 缓存,如果使用单向链表实现,则缓存访问的时间复杂度为 O(n),因为不管缓存有没有满,都需要遍历一遍链表。
可以继续优化这个实现思路,比如使用双向链表,并引入 哈希表(Hash table) 来记录每个数据的位置,将缓存访问的时间复杂度降到 O(1)。
代码
class Node {
// @param {number} key
// @param {number} value
constructor(key, value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class LRUCache {
// @param {number} capacity
constructor(capacity) {
this.cap = capacity;
this.cache = new Map();
this.head = new Node(0, 0);
this.tail = new Node(0, 0);
this.head.next = this.tail;
this.tail.prev = this.head;
}
// @param {number} key
// @return {number}
get(key) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
this.remove(this.cache.get(key));
this.insert(this.cache.get(key));
return this.cache.get(key).value;
}
return -1;
}
// @param {Node} node
remove(node) {
const prev = node.prev;
const next = node.next;
prev.next = next;
next.prev = prev;
}
// @param {Node} node
insert(node) {
const next = this.head.next;
this.head.next = node;
next.prev = node;
node.prev = this.head;
node.next = next;
}
// @param {number} key
// @param {number} value
// @return {void}
put(key, value) {
if (this.cache.has(key)) {
this.remove(this.cache.get(key));
}
this.cache.set(key, new Node(key, value));
this.insert(this.cache.get(key));
if (this.cache.size > this.cap) {
const old = this.tail.prev;
this.remove(old);
this.cache.delete(old.key);
}
}
}
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var obj = new LRUCache(capacity)
* var param_1 = obj.get(key)
* obj.put(key,value)
*/
